gs1 rain rfid RAIN uses the GS1 UHF Gen2 protocol which ISO/IEC has standardized as 18000-63. RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can .
Statewide coverage is the hallmark of the Auburn Sports Network's exclusive coverage of Auburn football. All home and away games are broadcast across the entire state of Alabama plus portions of .
0 · rain rfid technology
1 · rain rfid meaning
2 · gs1 rfid tag format
3 · gs1 rfid numbering
4 · gs1 rfid codes
5 · gs1 rfid
• Commentators Verne Lundquist and Gary Danielson called the game on television nationally for CBS's SEC coverage.Lundquist's call of the last play:On the way. no, returned by Chris Davis. Davis goes left, . See more
RAIN can use the GS1 UHF Gen2 protocol which ISO/IEC has standardized as 18000-63. The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to .RAIN uses the GS1 UHF Gen2 protocol which ISO/IEC has standardized as 18000-63. RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link .
GS1 standards are focused on UHF and HF passive RFID tags. The most broadly implemented tags in our industries are UHF passive tags, also known as RAIN RFID tags.Frequency: allocations authorised for RFID applications, specifically within the 860 to 960 MHz band of the UHF spectrum. Power: maximum wattage allowed for RFID, calculated as ERP (Effective Radiated Power) or EIRP (Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power)RAIN can use the GS1 UHF Gen2 protocol which ISO/IEC has standardized as 18000-63. The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed, and shared via the Internet.RAIN uses the GS1 UHF Gen2 protocol which ISO/IEC has standardized as 18000-63. RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can .
GS1 standards are focused on UHF and HF passive RFID tags. The most broadly implemented tags in our industries are UHF passive tags, also known as RAIN RFID tags.
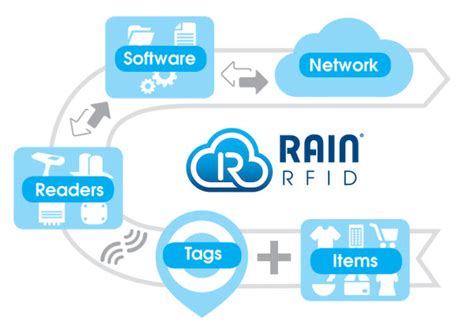
RAIN RFID systems help companies cut costs, improve customer service, reduce labor, increase accuracy and improve production throughput. The technology does not require user interaction and line-of-sight efforts, thereby leading to greater productivity and data collection accuracy.By using radio waves to automatically transmit data to a tag reader, RAIN RFID* helps brands ensure automatic, unique, and actionable product identification as well as interoperability with all trading partners along the supply chain.
GS1's EPC "Gen2" air interface protocol, first published by EPCglobal in 2004, defines the physical and logical requirements for an RFID system of interrogators and passive tags, operating in the 860 MHz - 930 MHz UHF range.
The GS1 Standards "Gen2" air interface protocol, first published by EPCglobal in 2004, defines the physical and logical requirements for an RFID system of interrogators and passive tags, operating in the 860 MHz - 960 MHz UHF range. It is now an ISO standard as well.
Larger warehouses often benefit from a RAIN RFID system because it can significantly increase the productivity of their processes. To read a barcode, a user must operate and position the scanner within sight of the item.This document is applicable to industry stakeholders such as solution providers, suppliers, processors, manufacturers, distributors, wholesalers, and operators. Specifically, this applies to stakeholders in the Foodservice industry using GS1 Standards and RAIN RFID technology.
Frequency: allocations authorised for RFID applications, specifically within the 860 to 960 MHz band of the UHF spectrum. Power: maximum wattage allowed for RFID, calculated as ERP (Effective Radiated Power) or EIRP (Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power)RAIN can use the GS1 UHF Gen2 protocol which ISO/IEC has standardized as 18000-63. The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed, and shared via the Internet.
RAIN uses the GS1 UHF Gen2 protocol which ISO/IEC has standardized as 18000-63. RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can . GS1 standards are focused on UHF and HF passive RFID tags. The most broadly implemented tags in our industries are UHF passive tags, also known as RAIN RFID tags.
RAIN RFID systems help companies cut costs, improve customer service, reduce labor, increase accuracy and improve production throughput. The technology does not require user interaction and line-of-sight efforts, thereby leading to greater productivity and data collection accuracy.By using radio waves to automatically transmit data to a tag reader, RAIN RFID* helps brands ensure automatic, unique, and actionable product identification as well as interoperability with all trading partners along the supply chain. GS1's EPC "Gen2" air interface protocol, first published by EPCglobal in 2004, defines the physical and logical requirements for an RFID system of interrogators and passive tags, operating in the 860 MHz - 930 MHz UHF range.
The GS1 Standards "Gen2" air interface protocol, first published by EPCglobal in 2004, defines the physical and logical requirements for an RFID system of interrogators and passive tags, operating in the 860 MHz - 960 MHz UHF range. It is now an ISO standard as well.
Larger warehouses often benefit from a RAIN RFID system because it can significantly increase the productivity of their processes. To read a barcode, a user must operate and position the scanner within sight of the item.
rain rfid technology
rain rfid meaning
$28.50
gs1 rain rfid|gs1 rfid numbering