which authentication protocol for smart card The FIDO authentication protocols are designed to allow robust authentication while providing . Have a look at the number 14 in the footnotes at the bottom of this link: iOS 14 - Apple. With that said, if the NFC tag isn't scanning automatically when using the associated .
0 · Smart Card Technology and the FIDO Protocols
1 · Smart Card Technical Reference
2 · Smart Card Architecture
Overview. The IOX-NFCREADERA lets you monitor vehicles based on their driver. Using Near Field Communication (NFC) with the Geotab GO device, identify drivers operating vehicles in a fleet at any given time. .
Vendors provide smart cards and smart card readers, and in many cases the vendors are different for the smart card and the smart card reader. Drivers for smart card readers are written to . See moreThe FIDO authentication protocols are designed to allow robust authentication while providing .
Storing the cryptographic keys in a secure central location makes the authentication process scalable and maintainable. For smart cards, Windows supports a provider architecture that meets the secure authentication requirements and is extensible so that you can include custom credential providers.The FIDO authentication protocols are designed to allow robust authentication while providing a superior user experience and protecting user privacy. They incorporate the following principles:
The CCID (Chip Card Interface Device) is a USB protocol that allows a smart card to be interfaced to a computer using a card reader which has a standard USB interface. This allows the smart card to be used as a security token for authentication and data encryption such as Bitlocker . When you use a password to sign in interactively to a domain account, Windows uses the Kerberos version 5 (v5) protocol for authentication. If you use a smart card, the operating system uses Kerberos v5 authentication with X.509 v3 certificates.Certificate Requirements and Enumeration: Learn about requirements for smart card certificates based on the operating system, and about the operations that are performed by the operating system when a smart card is inserted into the computer Learn how 1Kosmos enhances smart card authentication with BlockID, offering biometric-based security, identity proofing, privacy by design, distributed ledger technology, interoperability, and industry certifications.
The process: The user puts the smart card into a card reader hooked up to the device or system they want to use. The card reader talks to the smart card, asking the user to enter a password or give fingerprints to prove who they are.
A secret PIN. Authentication protocols are used to share the secret between the user and authenticator. The authenticator then either allows access or denies the requestor access. The authentication protocols that can be used in Windows Server 2003 environments are listed below: Kerberos version 5, used for network authentication.
EAP is used on encrypted networks to provide a secure way to send identifying information to provide network authentication. It supports various authentication methods, including as token cards, smart cards, certificates, one-time passwords and public key encryption.The user flow of smart card authentication is as follows. An employee’s identity is tied to company-deployed smart card, which has an embedded chip that is capable of storing and presenting cryptographic keys. Storing the cryptographic keys in a secure central location makes the authentication process scalable and maintainable. For smart cards, Windows supports a provider architecture that meets the secure authentication requirements and is extensible so that you can include custom credential providers.The FIDO authentication protocols are designed to allow robust authentication while providing a superior user experience and protecting user privacy. They incorporate the following principles:
The CCID (Chip Card Interface Device) is a USB protocol that allows a smart card to be interfaced to a computer using a card reader which has a standard USB interface. This allows the smart card to be used as a security token for authentication and data encryption such as Bitlocker . When you use a password to sign in interactively to a domain account, Windows uses the Kerberos version 5 (v5) protocol for authentication. If you use a smart card, the operating system uses Kerberos v5 authentication with X.509 v3 certificates.Certificate Requirements and Enumeration: Learn about requirements for smart card certificates based on the operating system, and about the operations that are performed by the operating system when a smart card is inserted into the computer Learn how 1Kosmos enhances smart card authentication with BlockID, offering biometric-based security, identity proofing, privacy by design, distributed ledger technology, interoperability, and industry certifications.
The process: The user puts the smart card into a card reader hooked up to the device or system they want to use. The card reader talks to the smart card, asking the user to enter a password or give fingerprints to prove who they are.A secret PIN. Authentication protocols are used to share the secret between the user and authenticator. The authenticator then either allows access or denies the requestor access. The authentication protocols that can be used in Windows Server 2003 environments are listed below: Kerberos version 5, used for network authentication.EAP is used on encrypted networks to provide a secure way to send identifying information to provide network authentication. It supports various authentication methods, including as token cards, smart cards, certificates, one-time passwords and public key encryption.

Smart Card Technology and the FIDO Protocols
Smart Card Technical Reference
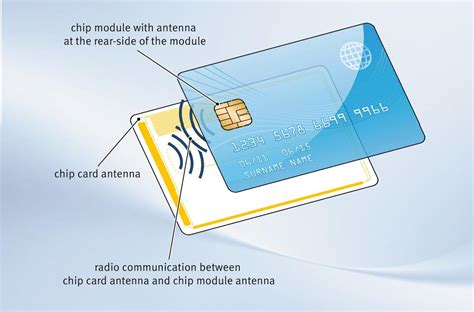
Smart Card Architecture

I was recommended anyone experiencing the same issue to rub their cards on the front and back of the I phone to see if the notifications come up if they do then obviously remove that card from your wallet or place it .
which authentication protocol for smart card|Smart Card Technical Reference