rfid tag cost sharing in the retail supply chain The average cost of an RFID tag has fallen by 80 percent to about four cents 1 in the last decade, while read accuracy has doubled and range more than quintupled (which allows for fewer devices and better reads). Even the prices of . The OLED hasn’t changed anything. The NFC reader is in the controller, and the operating system is the same on all updated models. I can’t give you a guarantee, but if people got .
0 · rfid use cases in retail
1 · rfid technology in retail
2 · rfid tags mckinsey
3 · rfid tags in retail
4 · rfid tag review
5 · rfid in stores
6 · retail rfid chain
7 · cost of rfid tags
First published: 25.07.2023 / Updated: 22.05.2024. 2023-07-25 2024-05-22. NFC21 GmbH. Merziger Str. 6. D-45481 Mülheim an der Ruhr. Germany. +49 208 / 60 70 42 0 .
In this research, we study some of the operational benefits of item-level radio . We analyze the effect of game modes and investment cost locations on firms’ . In this research, we study some of the operational benefits of item-level radio frequency identification (RFID), and how these benefits may affect the dynamics of the retailer-manufacturer interaction. We analyze the effect of game modes and investment cost locations on firms’ profits and their incentives to adopt Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. We consider a supply.
The average cost of an RFID tag has fallen by 80 percent to about four cents 1 in the last decade, while read accuracy has doubled and range more than quintupled (which allows for fewer devices and better reads). Even the prices of . In this research, we study some of the operational benefits of item-level radio frequency identification (RFID), and how these benefits may affect the dynamics of the retailer-manufacturer interaction.
RFID implementation in the supply chain faces two major challenges: adoption issues in supply chain processes and the cost of tags. Effective strategies in handling these challenges include precise and extensive modeling of supply chain processes and mass producing RFID tags.
Analyzing the proliferation of item‐level RFID, recent studies have identified the cost sharing of the technology as a gating issue. Various qualitative studies have predicted that conflict will arise, in particular in decentralized supply chains, from the fact that the benefits and the costs resulting from item‐level RFID are not . We analyze the impact of inventory inaccuracies and RFID tag costs on supply chain members’ optimal pricing decisions and maximum profits under different RFID adoption strategies. In addition, we characterize the equilibrium RFID adoption strategy under different tag costs and inventory availability rates. For this objective, we propose a novel revenue-cost-sharing (RCS) contract based on the bargaining game as the incentive to encourage the implementation, and numerical results show that the RCS contract is considerably more effective than the wholesale-price contract for supply chain coordination. This study presents an economic investment analysis by calculating the NPV of an RFID investment on a three-echelon supply chain using tagging cost sharing factors. Considering two cases, the effects of tagging cost sharing factor .
Walmart’s objective was to replace bar codes and scanners with RFID tags and readers to increase speed, efficiency, and security in the supply chain, and to reduce inventory levels, out-of-stock merchandise, and labor cost within the retail stores and warehouses. In this research, we study some of the operational benefits of item-level radio frequency identification (RFID), and how these benefits may affect the dynamics of the retailer-manufacturer interaction. We analyze the effect of game modes and investment cost locations on firms’ profits and their incentives to adopt Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. We consider a supply. The average cost of an RFID tag has fallen by 80 percent to about four cents 1 in the last decade, while read accuracy has doubled and range more than quintupled (which allows for fewer devices and better reads). Even the prices of .
In this research, we study some of the operational benefits of item-level radio frequency identification (RFID), and how these benefits may affect the dynamics of the retailer-manufacturer interaction.
RFID implementation in the supply chain faces two major challenges: adoption issues in supply chain processes and the cost of tags. Effective strategies in handling these challenges include precise and extensive modeling of supply chain processes and mass producing RFID tags.Analyzing the proliferation of item‐level RFID, recent studies have identified the cost sharing of the technology as a gating issue. Various qualitative studies have predicted that conflict will arise, in particular in decentralized supply chains, from the fact that the benefits and the costs resulting from item‐level RFID are not . We analyze the impact of inventory inaccuracies and RFID tag costs on supply chain members’ optimal pricing decisions and maximum profits under different RFID adoption strategies. In addition, we characterize the equilibrium RFID adoption strategy under different tag costs and inventory availability rates. For this objective, we propose a novel revenue-cost-sharing (RCS) contract based on the bargaining game as the incentive to encourage the implementation, and numerical results show that the RCS contract is considerably more effective than the wholesale-price contract for supply chain coordination.
This study presents an economic investment analysis by calculating the NPV of an RFID investment on a three-echelon supply chain using tagging cost sharing factors. Considering two cases, the effects of tagging cost sharing factor .
nfl all team standings
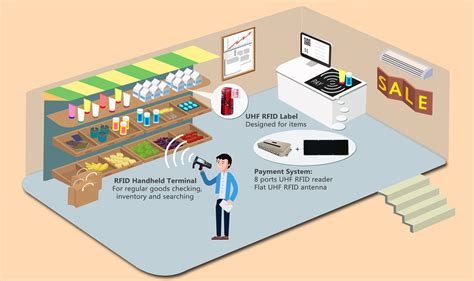
rfid use cases in retail
rfid technology in retail

1. Open your phone’s app store: Go to the app store on your smartphone. If you have an Android device, open the Google Play Store, and if you have an iPhone, open the App Store. 2. Search for an NFC reader app: In .With Cards - Mobile Wallet, you can add everything to your cards wallet, including loyalty, payment, access, identity, and transport cards. In .Contactless payments are transactions made by tapping a card or device with NFC over a terminal. Visa offers secure and convenient contactless payments at many merchants in the U.S. and abroad.
rfid tag cost sharing in the retail supply chain|rfid tag review