how to determine rfid sensor output RFID readers’ power output depends on two components. These are power output going into the antenna and antenna gain. Power going into the antenna (RF power) is usually indicated in milliwatt (mW) or in dBm. As with most new technologies, there were many early applications for NFC that never really got any traction. For instance, Google came up with Android Beam as an idea for exchanging . See more
0 · what are rfid sensors
1 · rfid sensors for beginners
2 · rfid sensor performance
3 · rfid antenna microchip
4 · microchip rfid sensor
5 · how rfid sensor works
6 · demystifying rfid sensor
7 · demystifying rfid
Dot., the connection company, has created a replacement with a straightforward website and NFC companion cards. The premise is straight forward: a plastic card with NFC inside and QR code backup on the back.
what are rfid sensors
To read an RFID sensor: The antenna emits radio waves that activate the microchip. The microchip modulates the radio waves to transmit its identification data. An RFID reader decodes the modulated signal to .
rfid sensors for beginners
To read an RFID sensor: The antenna emits radio waves that activate the microchip. The microchip modulates the radio waves to transmit its identification data. An RFID reader decodes the modulated signal to determine the . RFID readers’ power output depends on two components. These are power output going into the antenna and antenna gain. Power going into the antenna (RF power) is usually indicated in milliwatt (mW) or in dBm.
The process of identifying an asset using RFID involves three main components – the tag itself, a reader or scanner device, and a database or software system for storing and managing data. The first step is encoding information on to each unique tag before attaching it to an asset.Reader transmits power is the power sent out by the reader to the RFID antenna, while the system output power is the overall power transmitted by the RFID system. The antenna gain, cable losses, and the reader’s transmit power are all taken into consideration while deciding the RFID system output power.RFID components are powered by battery, so internal circuits can operate even when tag is outside reader/writer communication range (sensor is shown in blue in block diagram). Unlike passive and semi-passive RFID tags, active RFID tags generate their own radio frequency signals, enabling long-distance
While reader transmit power is the amount of power the reader sends out to the antenna, reader sensitivity is the lowest RSSI threshold at which a reader can detect a tag’s return signal. In laymen’s terms, reader sensitivity is the weakest tag .
This article discusses RFID technology and what designer should look for when designing an RFID application. We’ll look at how we can make use of COMSOL Multiphysics® simulation software to determine the operating read range of a passive RFID tag powered by a reader’s interrogating field. Additionally, we will look at how we can maximize this operating range by optimizing the tag’s antenna design.
rfid sensor performance
rfid antenna microchip
sdi smart card
In most RFID systems, it is recommended to test different settings for both transmit power and receive sensitivity in order to create the ideal read zone. But below I will provide two examples of applications that might lean toward using one over the other.
RFID Middleware Introduction. RFID general purposes input and outputs (GPIO) allow you to add sensors to your RFID readers and portals. Use light-stacks, buzzers, motion detectors with RFID.
To read an RFID sensor: The antenna emits radio waves that activate the microchip. The microchip modulates the radio waves to transmit its identification data. An RFID reader decodes the modulated signal to determine the . RFID readers’ power output depends on two components. These are power output going into the antenna and antenna gain. Power going into the antenna (RF power) is usually indicated in milliwatt (mW) or in dBm.
The process of identifying an asset using RFID involves three main components – the tag itself, a reader or scanner device, and a database or software system for storing and managing data. The first step is encoding information on to each unique tag before attaching it to an asset.Reader transmits power is the power sent out by the reader to the RFID antenna, while the system output power is the overall power transmitted by the RFID system. The antenna gain, cable losses, and the reader’s transmit power are all taken into consideration while deciding the RFID system output power.
RFID components are powered by battery, so internal circuits can operate even when tag is outside reader/writer communication range (sensor is shown in blue in block diagram). Unlike passive and semi-passive RFID tags, active RFID tags generate their own radio frequency signals, enabling long-distance While reader transmit power is the amount of power the reader sends out to the antenna, reader sensitivity is the lowest RSSI threshold at which a reader can detect a tag’s return signal. In laymen’s terms, reader sensitivity is the weakest tag . This article discusses RFID technology and what designer should look for when designing an RFID application.
We’ll look at how we can make use of COMSOL Multiphysics® simulation software to determine the operating read range of a passive RFID tag powered by a reader’s interrogating field. Additionally, we will look at how we can maximize this operating range by optimizing the tag’s antenna design. In most RFID systems, it is recommended to test different settings for both transmit power and receive sensitivity in order to create the ideal read zone. But below I will provide two examples of applications that might lean toward using one over the other.
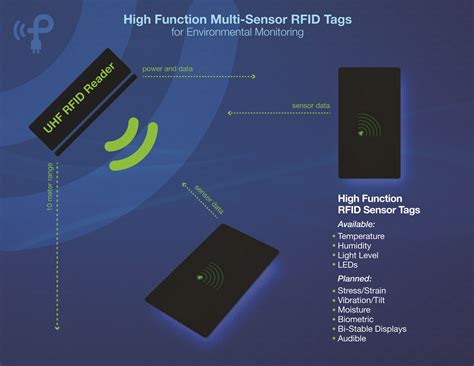
microchip rfid sensor
how rfid sensor works
Botw 23/24/25/26 Cards in 1 Nfc Game Cards Pack for the Legend of Zelda Breath of the Wild With Mini Crystal Case (NS Game Card Size) from $3.99 $8.99. 26 Cards in 1 Pack 25 Cards in 1 Pack 24 Cards in 1 Pack 23 Cards in .
how to determine rfid sensor output|rfid antenna microchip