rfid chip in 2019 Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical . The Auburn IMG Sports Network is the sports radio network for the Auburn Tigers, the athletic programs of Auburn University.Headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, United States, the radio .
0 · rfid microchip uses
1 · rfid implants
2 · rfid chip implants
3 · rfid chip implantation
4 · rfid chip images
5 · rfid chip for pets
6 · rfid chip failure rate
7 · emerging technology rfid
KAHI Audience Map - KAHI.com | The Voice of the Foothills

rfid microchip uses
Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical . Proponents of the chips say they're safe and largely protected from hacking, but one scientist is raising privacy concerns around the kind of . Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards. Proponents of the chips say they're safe and largely protected from hacking, but one scientist is raising privacy concerns around the kind of personal health data that might be stored on the.
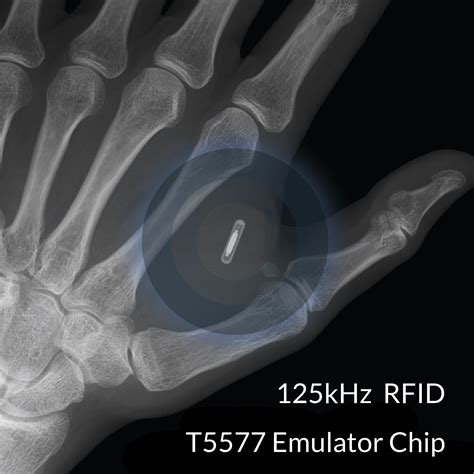
Here, we explain implanted RFID technology, its potential uses, and what is and is not known about its safety. We present images of a patient with an RFID chip who presented to our clinic for acute metacarpal and phalangeal fractures, to demonstrate the clinical and radiographic appearance of these chips. More commonly, RFID identification of humans is based on tags that are worn in e.g. hospital bracelets or RFID embedded identity cards (Gilleson et al., 2019; Rotter et al., 2008; Smith, 2008). The subcutaneous implantation of RFID chips is a .A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
The benefits of an implantable RFID chip, which is durable and about the size of a grain of rice, can hold or link to information about the identity, physiological characteristics, health . Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. By Haley Weiss. Professor Kevin Warwick holds up an RFID .To address this storage-of-data limitation, the silicon RFID chip was developed. Auto ID-based technologies such as optical barcodes and RFID address the function of "contactless" behavior, which eliminates the impracticalities of mechanical touch and enables the performance of . This study will review how human RFID microchip implants will impact and effect security, privacy, and ethical concerns associated with the new initiative for RFID implants to be used on human beings in everyday activities.
We present images of a patient with an RFID chip who presented to our clinic for acute metacarpal and phalangeal fractures, to demonstrate the clinical and radiographic appearance of these chips. Keywords: Hand microchip; MRI safety; RFID; . Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards. Proponents of the chips say they're safe and largely protected from hacking, but one scientist is raising privacy concerns around the kind of personal health data that might be stored on the.
Here, we explain implanted RFID technology, its potential uses, and what is and is not known about its safety. We present images of a patient with an RFID chip who presented to our clinic for acute metacarpal and phalangeal fractures, to demonstrate the clinical and radiographic appearance of these chips. More commonly, RFID identification of humans is based on tags that are worn in e.g. hospital bracelets or RFID embedded identity cards (Gilleson et al., 2019; Rotter et al., 2008; Smith, 2008). The subcutaneous implantation of RFID chips is a .
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
The benefits of an implantable RFID chip, which is durable and about the size of a grain of rice, can hold or link to information about the identity, physiological characteristics, health .

Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. By Haley Weiss. Professor Kevin Warwick holds up an RFID .
To address this storage-of-data limitation, the silicon RFID chip was developed. Auto ID-based technologies such as optical barcodes and RFID address the function of "contactless" behavior, which eliminates the impracticalities of mechanical touch and enables the performance of . This study will review how human RFID microchip implants will impact and effect security, privacy, and ethical concerns associated with the new initiative for RFID implants to be used on human beings in everyday activities.
rfid implants
1979 uno cards
Hold down the power button on your phone. Select the option to power off or restart your device. Wait for your phone to completely shut down. After a few seconds, press the power button again to turn your phone back on. .
rfid chip in 2019|rfid chip failure rate