name the three primary operating frequencies for rfid tags High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a . See more Listen to LSU Radio Stream Free – Leanstream. Mobile Menu Button. Sports. Baseball. Tickets Schedule Roster icon-facebook; icon-twitter; icon-instagram . Mike VII (Live Tiger)
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
3 · rfid radio frequency identification
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · radio frequency identification tags are
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
For background tag reading, iPhones can read URIs with specific URL schemes. Other NFC .
When referring to operating frequency, we generally refer to it in hertz (usually kilohertz or megahertz). A hertz is the standard measurement of a wave cycle (radio waves in this case). Imagine an ocean wave with a peak and a trough. A hertz measures a wave cycle by beginning with the midpoint from . See more
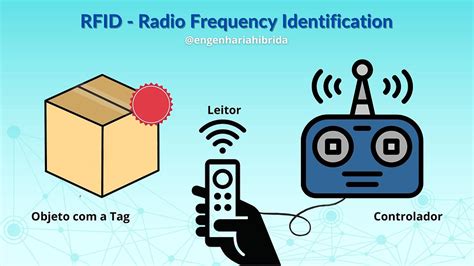
Low Frequency (LF) tags generally operate at 125–134kilohertz, meaning they usually have slower data transfer rates than their high . See moreHigh Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a . See moreThe majority of UHF systems operate between 860and 960megahertz. The distances for UHF tags are usually measured in feet and meters. While the tags are an excellent . See moreThis article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three .
RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post.This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency).
RFID tags operate at different frequencies: LF (Low Frequency) 125-134.2 kHz, HF (High Frequency) 13.56 MHz, and UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) 860-960 MHz. LF tags, with a short read range, are commonly used for access control and inventory management in retail and healthcare industries. Let’s delve into the three main RFID frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). Low-Frequency (LF) RFID operates in the frequency range of 30 kHz to 300 kHz. This frequency band provides short read range capabilities, typically up to a few centimeters.
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
Generally speaking, RFID systems are mainly divided into the following three types: LF RFID, HF RFID, and UHF RFID. The operating frequency of LF RFID is 125kHz-134.2 kHz. The operating frequency of HF RFID is 13.56MHz.RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)RFID technology can be classified into three main frequency categories: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). Each of these frequencies has its own advantages and limitations and is suitable for different applications.
RFID systems typically operate at three main frequency ranges: Low Frequency (LF): 30 kHz to 300 kHz. High Frequency (HF): 3 MHz to 30 MHz. Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): 300 MHz to 3 GHz. Each frequency range has its unique advantages and limitations, suited for different industrial applications.Understanding Tag Size and Read Range for RFID Systems: The read range of RFID tags determines the distance at which RFID readers can detect and read them, with factors such as tag frequency, antenna design, and environmental conditions influencing this range. RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post.This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency).
RFID tags operate at different frequencies: LF (Low Frequency) 125-134.2 kHz, HF (High Frequency) 13.56 MHz, and UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) 860-960 MHz. LF tags, with a short read range, are commonly used for access control and inventory management in retail and healthcare industries. Let’s delve into the three main RFID frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). Low-Frequency (LF) RFID operates in the frequency range of 30 kHz to 300 kHz. This frequency band provides short read range capabilities, typically up to a few centimeters.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.Generally speaking, RFID systems are mainly divided into the following three types: LF RFID, HF RFID, and UHF RFID. The operating frequency of LF RFID is 125kHz-134.2 kHz. The operating frequency of HF RFID is 13.56MHz.
RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)RFID technology can be classified into three main frequency categories: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). Each of these frequencies has its own advantages and limitations and is suitable for different applications.
RFID systems typically operate at three main frequency ranges: Low Frequency (LF): 30 kHz to 300 kHz. High Frequency (HF): 3 MHz to 30 MHz. Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): 300 MHz to 3 GHz. Each frequency range has its unique advantages and limitations, suited for different industrial applications.

what frequency does rfid use
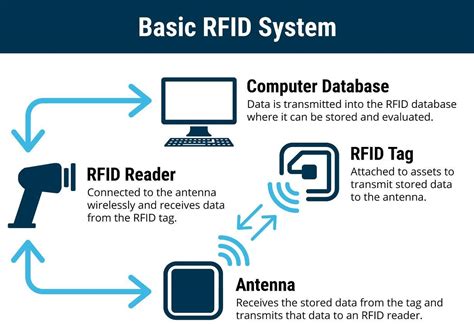
contactless cards data

NFC Smart Card Readers with Wiegand26/34 Output. Model No.: PCD-02NFC. What is NFC .:octocat: :credit_card: NFC Reader And Writer using Android devices by @romellfudi - GitHub - romellfudi/FudiNFC: :octocat: NFC Reader And Writer using Android devices by @romellfudi
name the three primary operating frequencies for rfid tags|rfid frequency chart