rfid tag architecture diagram RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be read from several meters away, without requiring direct line-of .
The Android Smart Card Emulator has the following dependencies: NFC hardware built into the smartphone for HCE. Android 4.4 “KitKat” (or newer) or CyanogenMod 11 (or newer) permissions for a data connection .
0 · what is rfid
1 · types of rfid tags
2 · rfid technology
3 · rfid data identification
4 · rfid block diagram reader
5 · rfid bar code
6 · rfid architecture pdf
7 · best practices for rfid tags
There’s a £7 or £5 upfront charge for each standard or visitor card. Cards must be topped up before travel. You can’t use Oyster cards in taxis. An Oyster card is a payment card, like contactless, but differs because it is .
what is rfid
The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the .A simplified block schematic of an RFID tag (also called transponder) is shown in the diagram .
types of rfid tags
RFID component parts are: Tag or transponder: a RFID tag is a tiny radio device that is also .
Picture of the proposed SDR RFID tag [architecture (a), see Fig. 1]. The tag is composed of an .
The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the objects to be uniquely identified. The RFID reader is a device that transmits and receives data through radio waves using the connected antennas. Its functions include powering the tag, and reading/writing data to the tag.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be read from several meters away, without requiring direct line-of .
A simplified block schematic of an RFID tag (also called transponder) is shown in the diagram below. Various components of the tag are as shown. Normally, the antenna is external to the tag chip, and large in size.RFID component parts are: Tag or transponder: a RFID tag is a tiny radio device that is also referred to as a transponder, smart tag, smart label or radio bar code. The tag comprises a simple silicon microchip (typically less than half a millimetre in size) attached to a small flat aerial and mounted on a substrate.
Picture of the proposed SDR RFID tag [architecture (a), see Fig. 1]. The tag is composed of an envelope detector and a backscattering modulator both connected to the Arduino platform.
rfid technology
Module 2 – RFID Architecture Components. Main Objectives: Know components of RFID systems: Reader (also known as an Interrogator) – to read and write to tags. One or more reader antennas – transmits the reader power and commands to tags and receives data from tags.This section is written for RF coil designers and RFID system engineers. It reviews basic electromagnetic theories on antenna coils, a procedure for coil design, calculation and measurement of inductance, an antenna tuning method, and read range in RFID applications. 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.As schowing in figure 1 the architecture of RFID tag is constituted by modulation / demodulation bloc, a local memory containing information about product stored in data base, and a.RFID system architecture as in Fig. 2 consists of three entities: back-end server, RFID reader and RFID tag [15,16]. An RFID tag contains an antenna to receive and send signal and short.
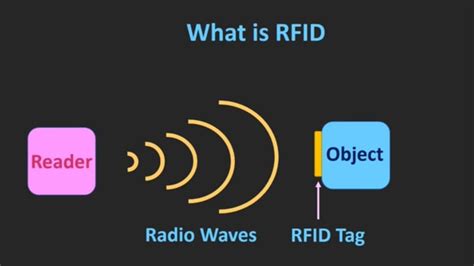
The RFID system architecture consists of a reader and a tag (also known as a labelor chip). The reader queries the tag, obtains information, and then takes action based on that information. The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the objects to be uniquely identified. The RFID reader is a device that transmits and receives data through radio waves using the connected antennas. Its functions include powering the tag, and reading/writing data to the tag. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be read from several meters away, without requiring direct line-of .
A simplified block schematic of an RFID tag (also called transponder) is shown in the diagram below. Various components of the tag are as shown. Normally, the antenna is external to the tag chip, and large in size.
RFID component parts are: Tag or transponder: a RFID tag is a tiny radio device that is also referred to as a transponder, smart tag, smart label or radio bar code. The tag comprises a simple silicon microchip (typically less than half a millimetre in size) attached to a small flat aerial and mounted on a substrate.
Picture of the proposed SDR RFID tag [architecture (a), see Fig. 1]. The tag is composed of an envelope detector and a backscattering modulator both connected to the Arduino platform.Module 2 – RFID Architecture Components. Main Objectives: Know components of RFID systems: Reader (also known as an Interrogator) – to read and write to tags. One or more reader antennas – transmits the reader power and commands to tags and receives data from tags.This section is written for RF coil designers and RFID system engineers. It reviews basic electromagnetic theories on antenna coils, a procedure for coil design, calculation and measurement of inductance, an antenna tuning method, and read range in RFID applications. 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.As schowing in figure 1 the architecture of RFID tag is constituted by modulation / demodulation bloc, a local memory containing information about product stored in data base, and a.
RFID system architecture as in Fig. 2 consists of three entities: back-end server, RFID reader and RFID tag [15,16]. An RFID tag contains an antenna to receive and send signal and short.
what device has a rfid chip reader

rfid data identification
rfid block diagram reader
rfid bar code
The Remote Smart Card Reader has the following dependencies: NFC hardware built into the smartphone. Android 4.4 “KitKat” or CyanogenMod 11 (or newer) permissions for a data connection (communication with vpcd) and for using .NFC RFID Smart Card Reader Writer RFID Copier Duplicator ID Card Reader Writer 512kb Memory NFC Card Reader Kit (1 T5577 Card 3 UID Cards and 1 UID Key Fob) 2.6 out of 5 .
rfid tag architecture diagram|rfid data identification