what is difference between rf id frequencies Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader. This number can be used to track inventory goods. Relive the 2002 Wild Card matchup between the Green Bay Packers and the Atlanta Falcons by watching this full game replay brought to you by NFL Game Pass. video.
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid reader
2 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
3 · rfid frequency ranges
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · rfid definition for dummies
6 · how does rfid tags work
7 · how does an rfid work
SentinelX NFC Overview. The newest addition to the SentinelX family, the .
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.Understanding the differences in RFID frequencies is particularly important when choosing t.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader. This number can be used to track inventory goods.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.Understanding the differences in RFID frequencies is particularly important when choosing the right RFID solution. This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), .
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware. RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post.Explore. How to Select a Correct Tag – Frequency. RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)
Country of Deployment. Different countries allocate different bands of the radio spectrum for RFID, so no single technology optimally satisfies all the requirements of existing and potential markets. The industry has worked diligently to standardize three main RF bands - low frequency, high frequency, and ultra-high frequency.RFID has the capability to automate and enhance workflows and improve operational efficiencies, specifically in healthcare and life science organizations. However, there are different types of RFID technologies and their differences affect market adoption and outcomes.HF Frequency Range – The high frequency spectrum comprises of frequencies ranging between 3 MHz and 30 MHz, but there is only one frequency of 13.56 MHz that can be utilized for RFID applications. The frequency is now accessible for RFID .
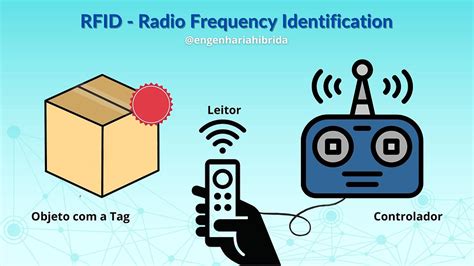
what frequency does rfid use
This article provides a guide on RFID Frequency Ranges: LF, HF, UHF, and Microwave. We will explore how these frequencies enable a variety of applications, providing clarity to make informed decisions in the exciting world of radio frequency identification.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.
Understanding the differences in RFID frequencies is particularly important when choosing the right RFID solution. This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), .
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.
RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post.Explore. How to Select a Correct Tag – Frequency. RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave) Country of Deployment. Different countries allocate different bands of the radio spectrum for RFID, so no single technology optimally satisfies all the requirements of existing and potential markets. The industry has worked diligently to standardize three main RF bands - low frequency, high frequency, and ultra-high frequency.
RFID has the capability to automate and enhance workflows and improve operational efficiencies, specifically in healthcare and life science organizations. However, there are different types of RFID technologies and their differences affect market adoption and outcomes.HF Frequency Range – The high frequency spectrum comprises of frequencies ranging between 3 MHz and 30 MHz, but there is only one frequency of 13.56 MHz that can be utilized for RFID applications. The frequency is now accessible for RFID .
ultra high frequency rfid reader
hell-bent carbon fiber wallet with rfid protection
ultra thin rfid protected leather wallet case
renwick backpack rfid protection
rfid radio frequency identification tags
$11.99
what is difference between rf id frequencies|rfid frequency ranges