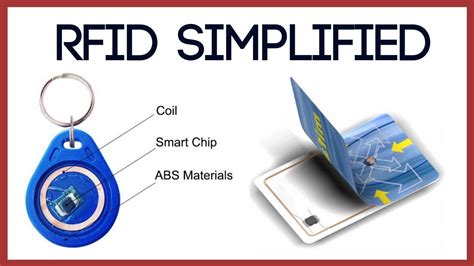
chip rfid 2015 InfectionInfection has been cited as a source of failure within RFID and related microchip implanted individuals, either due to improper implantation techniques, implant rejections or corrosion of implant elements. See more For example, if I currently use an RFID reader to track the locations of items in .NFC enabled phones can ONLY read NFC and passive high frequency RFID (HF-RFID). These must be read at an extremely close range, .
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · types of rfid chips
2 · rfid chips in humans
3 · rfid chips for sale
4 · rfid chip pros and cons
5 · rfid chip meaning
6 · rfid chip manufacturing
7 · pros and cons of rfid
Angie Ward was born La Jolla, California . She graduated from Colonial Hills Christian School in 1986, Jefferson State College in 1990, and Auburn University in 1992. Ward grew up on a horse farm in Alpharetta, GA. Her parents Marvin and Audrey, and sister Amanda owned and operate Ward Stables located north of Atlanta, one of the top American Saddlebred Training facilities in the Southeastern United States. Father Marvin Ward is a memb.
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. This type of subdermal implant usually contains a . See more• 1998: The first experiments with a radio-frequency identification (RFID) implant were carried out in 1998 by the British scientist Kevin Warwick. . See more
• Brain implant• Skin• Dental implant See moreFor Microchip implants that are encapsulated in silicate glass, there exists multiple methods to embed the device subcutaneously ranging from placing the microchip implant in a syringe or trocar and piercing under the flesh (subdermal) then releasing the . See more
InfectionInfection has been cited as a source of failure within RFID and related microchip implanted individuals, either due to improper implantation techniques, implant rejections or corrosion of implant elements. See moreDespite a lack of evidence demonstrating invasive use or even technical capability of microchip implants, they have been the subject of many conspiracy theories.The Southern Poverty Law Center reported in 2010 that on the Christian right, there were concerns that . See moreA few jurisdictions have researched or preemptively passed laws regarding human implantation of microchips.United StatesIn the United States, many states such as Wisconsin (as . See moreThe general public are most familiar with microchips in the context of identifying pets.In popular cultureImplanted individuals are considered to be grouped together as part of the transhumanism See more
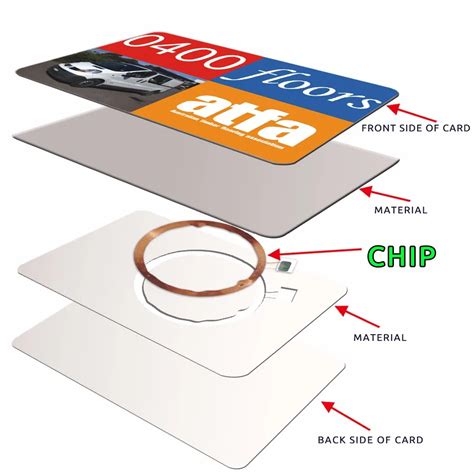
NXP Semiconductors launched the NXP ICODE® chip series as a high-frequency (HF) RFID product. It is designed to meet the needs of modern supply chain and asset management. The .
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
NXP Semiconductors launched the NXP ICODE® chip series as a high-frequency (HF) RFID product. It is designed to meet the needs of modern supply chain and asset management. The ICODE chip uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz and targets medium to short-range RFID applications. Its core features include high-speed data transmission, strong anti . Biohax’s RFID chip was first offered to workers at Swedish tech hub Epicenter in January 2015. Since then the use of Biohax’s chip has expanded from simple office tasks such as opening doors and operating printers to payment for train journeys with one of . One chip recipient named Drew Andresen even rigged his car so that he can unlock it and start the engine with the chip in his hand: Drew starts his car using a RFID chip he got injected into. Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms, a.
Health Care Based Human RFID Implants. RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7).RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.The RFID chip will make individual player information accessible to the public. The data will be available via the NFL 2015 app. [112] The RFID chips are manufactured by Zebra Technologies. Zebra Technologies tested the RFID chip in 18 stadiums last year [when?] to . As the impact and influence of chip implants increases in the U.S., it's time to raise ethical and legal questions about this technology.
From Chip-Based to Chipless RFID Sensors: A Review Abstract: Radio frequency identification (RFID) sensors have received increasing attention in recent years due to their wireless battery-free operation, low profile, simplicity, low cost, and multimodality sensitivity.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.NXP Semiconductors launched the NXP ICODE® chip series as a high-frequency (HF) RFID product. It is designed to meet the needs of modern supply chain and asset management. The ICODE chip uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz and targets medium to short-range RFID applications. Its core features include high-speed data transmission, strong anti .
Biohax’s RFID chip was first offered to workers at Swedish tech hub Epicenter in January 2015. Since then the use of Biohax’s chip has expanded from simple office tasks such as opening doors and operating printers to payment for train journeys with one of . One chip recipient named Drew Andresen even rigged his car so that he can unlock it and start the engine with the chip in his hand: Drew starts his car using a RFID chip he got injected into. Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms, a.
Health Care Based Human RFID Implants. RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7).RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.
where are rfid chips used
types of rfid chips
The RFID chip will make individual player information accessible to the public. The data will be available via the NFL 2015 app. [112] The RFID chips are manufactured by Zebra Technologies. Zebra Technologies tested the RFID chip in 18 stadiums last year [when?] to .
As the impact and influence of chip implants increases in the U.S., it's time to raise ethical and legal questions about this technology.
rfid chips in humans
rfid chips for sale
rfid chip pros and cons

Go to the "Settings" app on your iPhone. Scroll down and tap on "Wallet & Apple Pay." On the "Wallet & Apple Pay" screen, you'll see an option to turn on "NFC Scanning or NFC tag reader." Toggle this switch to the "On" .
chip rfid 2015|rfid chip meaning