how do passive rfid tags get power Once the passive RFID tag is powered by the electromagnetic energy from the reader, it uses a process called backscatter communication to send data back to the reader. The tag modulates the reader’s signal by reflecting or absorbing portions of the radio wave. NFC. Homey can read NFC cards like your public transport card. This feature has a lot of .
0 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
1 · rfid is involved when using
2 · rfid active and passive tags
3 · radio frequency identification tags are
4 · long range passive rfid tags
5 · do rfid tags need batteries
6 · active vs passive rfid tags
7 · active rfid tags and readers
Locate and tap the "Settings" app, represented by a gear icon, to access the .
Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and .
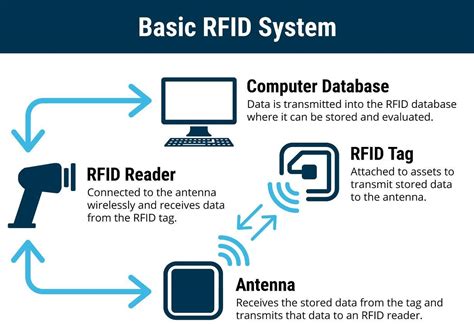
Once the passive RFID tag is powered by the electromagnetic energy from the reader, it uses a process called backscatter communication to send data back to the reader. The tag modulates the reader’s signal by reflecting or absorbing portions of the radio wave.Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader. Unlike their active counterparts, passive RFID tags do not have an internal power source. Instead, they draw energy from the RFID reader's electromagnetic wave to function. This makes them smaller, more cost-effective, and maintenance-free.Discover how passive RFID tags harness power from external signals without batteries. Learn about inductive coupling, capacitive coupling, and resonant inductive coupling, and explore their applications and future trends. Read our in-depth guide to understand passive RFID technology.
Among them, RFID passive tags are more widely used, especially in scenarios that require large-scale deployment. This article will focus on analyzing RFID passive tag, exploring their working principles, advantages, application fields, and limitations, to . Passive RFID tags rely on external RF energy emitted by RFID readers to power their operation. These tags are cost-effective, lightweight, and suitable for short-range applications. They are commonly used in access control, inventory management, and item tracking within a limited area.
Passive RFID tags do not have their own power source. Instead, they rely on the power supplied by the RFID reader to operate. When the RFID reader emits radio waves, the passive tag’s antenna captures the energy and uses it to power the microchip and send back the stored data to the reader.Passive RFID technology works by using radio waves to communicate between a tag and a reader. Unlike active tags, which require battery power, passive RFID tags do not require batteries and instead rely on radio waves emitted by the reader to power and transmit data.
How Does RF Field Power Impact Passive RFID? Passive RFID tags derive all of their operating power from the energy of the RF field as absorbed by their antennae.
Active RFID tags, distinguished by their internal power source, operate using a battery to actively transmit signals to RFID readers. The inclusion of a power source empowers active tags to broadcast signals over longer distances, enabling read ranges that can extend up to hundreds of meters.Once the passive RFID tag is powered by the electromagnetic energy from the reader, it uses a process called backscatter communication to send data back to the reader. The tag modulates the reader’s signal by reflecting or absorbing portions of the radio wave.Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader.
Unlike their active counterparts, passive RFID tags do not have an internal power source. Instead, they draw energy from the RFID reader's electromagnetic wave to function. This makes them smaller, more cost-effective, and maintenance-free.Discover how passive RFID tags harness power from external signals without batteries. Learn about inductive coupling, capacitive coupling, and resonant inductive coupling, and explore their applications and future trends. Read our in-depth guide to understand passive RFID technology.Among them, RFID passive tags are more widely used, especially in scenarios that require large-scale deployment. This article will focus on analyzing RFID passive tag, exploring their working principles, advantages, application fields, and limitations, to . Passive RFID tags rely on external RF energy emitted by RFID readers to power their operation. These tags are cost-effective, lightweight, and suitable for short-range applications. They are commonly used in access control, inventory management, and item tracking within a limited area.
Passive RFID tags do not have their own power source. Instead, they rely on the power supplied by the RFID reader to operate. When the RFID reader emits radio waves, the passive tag’s antenna captures the energy and uses it to power the microchip and send back the stored data to the reader.Passive RFID technology works by using radio waves to communicate between a tag and a reader. Unlike active tags, which require battery power, passive RFID tags do not require batteries and instead rely on radio waves emitted by the reader to power and transmit data.How Does RF Field Power Impact Passive RFID? Passive RFID tags derive all of their operating power from the energy of the RF field as absorbed by their antennae.

rfid radio frequency identification tags

emv smart card reader octopus box

Identiv’s uTrust 4701 F is the ideal combination of contact, contactless, and .
how do passive rfid tags get power|rfid active and passive tags