smart card protocol t 0 Created in 2005. According to its abstract, it specifies the operating conditions of an integrated circuit card that provides a USB interface. An integrated circuit card with a USB interface is named USB-ICC. ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 specifies: • the electrical conditions when a USB-ICC is operated by an interface device - for those contact . Try clearing the cache of the NFC service on your Android phone and check if this fixes your issue. Here’s how you can clear the cache of the NFC service on your Android device: Step 1: Open the .
0 · T=0 Protocol
1 · Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level
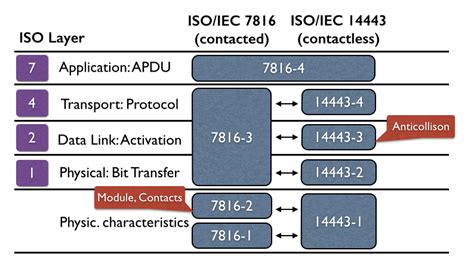
2 · ISO/IEC 7816
3 · ATR (Answer to Reset)
4 · 35.6.3.6 ISO 7816 for Smart Card Interfa
5 · 12.2.4.10 ISO7816
Operating frequency at 13.56MHz in accordance With ISO15693, ISO14443A/B, NFC and ISO18000-3 standards. Identification distance could be up to 30cm .It supports 13.56Mhz ISO14443A Read/Write chips: Mifare 1K/ Mifare 4K/ Mifare .
To have a T=0 or T=1 communication, both the card and the reader must support it. Most of nowaday cards support only T=1 and most of readers support both protocol. –Created in 2005. According to its abstract, it specifies the operating conditions of an integrated circuit card that provides a USB interface. An integrated circuit card with a USB interface is named USB-ICC. ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 specifies: • the electrical conditions when a USB-ICC is operated by an interface device - for those contact .
To have a T=0 or T=1 communication, both the card and the reader must support it. Most of nowaday cards support only T=1 and most of readers support both protocol. –
smart card tv ci+
If an APDU command response pair has been defined for T=0 and it has both command data and response data (case 4S) then a separate TPDU will be generated to send and receive data (GET RESPONSE). See chapter 12.2.1 of ISO/IEC 7816-3 (2006).ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 provides two protocols for control transfers. This is to support the protocol T=0 (version A) or to use the transfer on APDU level (version B). ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 provides the state diagrams for the USB-ICC for each of the transfers (bulk transfers, control transfers version A and version B). All EMV-compliant smart cards must support the T=0 or T=1 protocols, while terminals must support both. Immediately after a card is inserted into a terminal and while all contacts are maintained in a "low" state, supply voltage is applied to the card's V CC contact.The SERCOM USART features an ISO/IEC 7816-compatible operating mode. This mode permits interfacing with smart cards and Security Access Modules (SAM) communicating through an ISO 7816 link. Both T=0 and T=1 protocols defined by the ISO 7816 specification are supported.
The T=0 transmission protocol was first used in France during the initial development of smart cards, and it was also the first internationally standardized smart card protocol. It was generated in the early years of smart card technology, and it is thus designed for minimum memory usage and maximum simplicity.
T=0 Protocol
Exchange Information: Exchange information with the card based on T=0 (half-duplex transmission of characters) or T=1 (half-duplex transmission of blocks) protocol. Deactivation: Deactivate the smart card.The specifications permit two transmission protocols: character protocol (T=0) or block protocol (T=1). A card may support either but not both. (Note: Some card manufacturers adhere to neither of these protocols.

ISO7816 3.5 Protocol type T=0, asynchronous half duplex character transmission protocol. This clause defines the structure and processing of commands initiated by an interface device for transmission control and for card specific control in an asynchronous half duplex character transmission protocol.The SERCOM USART features an ISO/IEC 7816-compatible operating mode. This mode permits interfacing with smart cards and Security Access Modules (SAM) communicating through an ISO 7816 link. Both T=0 and T=1 protocols defined by the ISO 7816 specification are supported.
To have a T=0 or T=1 communication, both the card and the reader must support it. Most of nowaday cards support only T=1 and most of readers support both protocol. –
If an APDU command response pair has been defined for T=0 and it has both command data and response data (case 4S) then a separate TPDU will be generated to send and receive data (GET RESPONSE). See chapter 12.2.1 of ISO/IEC 7816-3 (2006).ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 provides two protocols for control transfers. This is to support the protocol T=0 (version A) or to use the transfer on APDU level (version B). ISO/IEC 7816-12:2005 provides the state diagrams for the USB-ICC for each of the transfers (bulk transfers, control transfers version A and version B).
All EMV-compliant smart cards must support the T=0 or T=1 protocols, while terminals must support both. Immediately after a card is inserted into a terminal and while all contacts are maintained in a "low" state, supply voltage is applied to the card's V CC contact.
The SERCOM USART features an ISO/IEC 7816-compatible operating mode. This mode permits interfacing with smart cards and Security Access Modules (SAM) communicating through an ISO 7816 link. Both T=0 and T=1 protocols defined by the ISO 7816 specification are supported.The T=0 transmission protocol was first used in France during the initial development of smart cards, and it was also the first internationally standardized smart card protocol. It was generated in the early years of smart card technology, and it is thus designed for minimum memory usage and maximum simplicity.Exchange Information: Exchange information with the card based on T=0 (half-duplex transmission of characters) or T=1 (half-duplex transmission of blocks) protocol. Deactivation: Deactivate the smart card.
The specifications permit two transmission protocols: character protocol (T=0) or block protocol (T=1). A card may support either but not both. (Note: Some card manufacturers adhere to neither of these protocols. ISO7816 3.5 Protocol type T=0, asynchronous half duplex character transmission protocol. This clause defines the structure and processing of commands initiated by an interface device for transmission control and for card specific control in an asynchronous half duplex character transmission protocol.
smart card vs micro chip

Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level
ISO/IEC 7816
smart card two-factor authentication
ATR (Answer to Reset)
Using an iPhone 4S with the iCarte case to read and write NFC tagsApp is NFC Tags, available on the App Store: http://itunes.apple.com/au/app/nfc-tags/id4995.
smart card protocol t 0|T=0 Protocol