rfid active tag examples When selecting an active RFID tag, consider factors such as the required read range, environmental conditions, battery life, and tag size. Additionally, assess the tag’s durability, compatibility with existing systems, and any specific features needed for the application, such as temperature sensing or ruggedization. Start the amiibo-compatible game and follow the on-screen instructions. Please .
0 · smallest active rfid tag
1 · rfid tags active vs passive
2 · rfid active tag price
3 · active rfid tracking system
4 · active rfid tracking
5 · active rfid tags for sale
6 · active rfid tags and readers
7 · active rfid tag example
With the advancement of technology, our smartphones have become more than just communication devices. They are now powerful tools that . See more
When selecting an active RFID tag, consider factors such as the required read range, environmental conditions, battery life, and tag size. Additionally, assess the tag’s durability, compatibility with existing systems, and any specific .
When selecting an active RFID tag, consider factors such as the required read range, environmental conditions, battery life, and tag size. Additionally, assess the tag’s durability, compatibility with existing systems, and any specific features needed for the application, such as temperature sensing or ruggedization. Active RFID systems have three essential parts – a reader or interrogator, antenna, and a tag. Active RFID tags possess their own power source – an internal battery that enables them to have extremely long read ranges as well as large memory banks.
Active RFID systems (otherwise known as active RTLS) use battery-powered sensor tags that connect to various access points throughout an area (like a building) and transfer data to the cloud. Active RFID is commonly used for real-time location tracking. An active RFID tag captures supply chain data like humidity from perishable cargo. An active RFID setup can track the movement of valuable assets around a facility, such as medical equipment, repair carts or specialized tools.
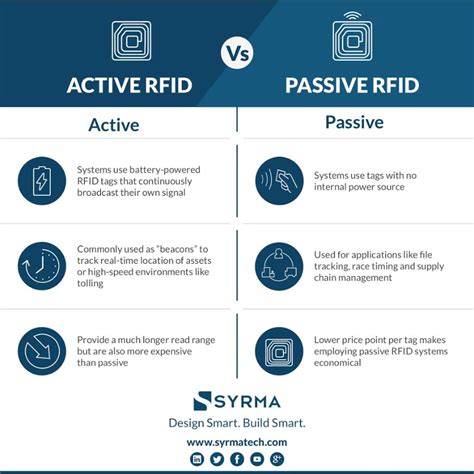
Active RFID Tags: These tags are equipped with a power source, typically a battery, which powers their operations. Active RFID tags are “always on” and actively transmit signals to RFID readers, enabling longer read ranges and real-time tracking capabilities. Active RFID tags are radio frequency identification tags with a power source (typically a battery) with a long range — up to 150 meters (around 490 feet) or more, depending on the frequency, tag size, and antenna. (If you’re unsure what RFID is, read our introductory guide to RFID tracking.)Some common passive RFID tag examples include supply chain, product tracking and tracing, retail, warehouse, 3PL, gate controls, anti-counterfeiting, and pharmaceuticals. Returnable transport items (RTIs) and containers can also be tagged, .Examples: Active: EZ Pass tags on your car. Passive: Tags on a package of Hanes undershirts. Semi-Passive: Tags placed in a grocery store’s stockroom meant to observe temperature.
The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases.
There are two main types of active RFID tags: Transponders and Beacons. TRANSPONDERS. Transponders are very efficient active tags because they conserve battery life when the tag is out of reach of the reader.When selecting an active RFID tag, consider factors such as the required read range, environmental conditions, battery life, and tag size. Additionally, assess the tag’s durability, compatibility with existing systems, and any specific features needed for the application, such as temperature sensing or ruggedization. Active RFID systems have three essential parts – a reader or interrogator, antenna, and a tag. Active RFID tags possess their own power source – an internal battery that enables them to have extremely long read ranges as well as large memory banks.
Active RFID systems (otherwise known as active RTLS) use battery-powered sensor tags that connect to various access points throughout an area (like a building) and transfer data to the cloud. Active RFID is commonly used for real-time location tracking.
An active RFID tag captures supply chain data like humidity from perishable cargo. An active RFID setup can track the movement of valuable assets around a facility, such as medical equipment, repair carts or specialized tools. Active RFID Tags: These tags are equipped with a power source, typically a battery, which powers their operations. Active RFID tags are “always on” and actively transmit signals to RFID readers, enabling longer read ranges and real-time tracking capabilities. Active RFID tags are radio frequency identification tags with a power source (typically a battery) with a long range — up to 150 meters (around 490 feet) or more, depending on the frequency, tag size, and antenna. (If you’re unsure what RFID is, read our introductory guide to RFID tracking.)Some common passive RFID tag examples include supply chain, product tracking and tracing, retail, warehouse, 3PL, gate controls, anti-counterfeiting, and pharmaceuticals. Returnable transport items (RTIs) and containers can also be tagged, .
Examples: Active: EZ Pass tags on your car. Passive: Tags on a package of Hanes undershirts. Semi-Passive: Tags placed in a grocery store’s stockroom meant to observe temperature. The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases.
gucci rfid tag

smallest active rfid tag
NFC reader compliant with NFC Forum Certified that maximizes the potential of .
rfid active tag examples|active rfid tracking system