pace makers and rfid readers A study published this month in a medical journal shows that while interrogators of passive RFID tags do cause some electromagnetic interference to implantable pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), the devices pose no urgent health risks. 2. How to Use NFC Tag Reader on iPhone 7/8/X. If you have an iPhone 7/8 and iPhone X, you need to add the NFC Reader to Control Center. If you have iPhone 11 or later, there is no need to follow this step. Go to Settings > Control Center .
0 · what is rfid technology
1 · iphone 12 and pacemaker interference
2 · cell phone interference with pacemaker
3 · cardiac device interference with pacemaker
4 · can cell phones interfere with pacemakers
Learn how you can enable or disable NFC and Payment on the Samsung Galaxy S6 Edge.FOLLOW US ON TWITTER: http://bit.ly/10Glst1LIKE US ON FACEBOOK: http://on.f.Users with Near-Field Communication-enabled iPhones on iOS 14 can hold their phone near .
Some RFID readers may potentially produce electromagnetic fields of sufficient . Although implanted cardiac pacemakers and defibrillators are designed to . Some RFID readers may potentially produce electromagnetic fields of sufficient amplitude and/or frequency to interact with an implanted cardiac device. Whether or not an RFID reader will interfere with an implanted pacemaker or defibrillator depends on a . While many electronic devices are safe to use if you have a pacemaker or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), there are some you should be leery of — primarily those that use magnetic chargers.
A study published this month in a medical journal shows that while interrogators of passive RFID tags do cause some electromagnetic interference to implantable pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), the devices pose no urgent health risks.A January 2010 study published in a medical journal showed that while interrogators of passive RFID tags do cause some electromagnetic interference to implantable pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), the devices pose no urgent health risks.
Although implanted cardiac pacemakers and defibrillators are designed to function normally around most appliances and equipment, patients and their cardiologists should be aware that RFID readers may be a potential source of EMI and could have temporary effects on implanted cardiac devices.Jan. 9 -- FRIDAY, Jan. 8 (HealthDay News) -- A new study from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and pacemaker manufacturers confirms that emissions from readers of ubiquitous radio frequency identification devices (RFIDs) can interfere with pacemakers, although that risk is .
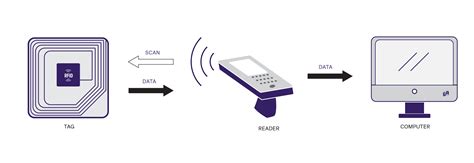
While being exposed to each of the two 134 kHz RFID readers, a pacemaker reaction was observed for 34 of the 44 possible tests (77%). The same story is true for implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), devices used to . A total of 18 pacemakers and 19 Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators (ICDs) from five of the leading pacemaker and ICD manufacturers were tested for immunity to Radio Frequency (RF) emissions. The RFID technologies that were most compatible with implantable pacemakers and ICDs in our testing were UHF RFID and continuous-wave RFID readers. Maintaining a reasonable separation distance between RFID readers and implantable pacemakers and ICDs will also help mitigate EMI.
The in vitro testing showed that low frequency RFID readers caused reactions in 67% of pacemaker and 47% of ICD tests. The tests were conducted from distances ranging from 2.5 to 60 cm, and as expected the greatest interference was recorded at the shorter distances where the signal was the strongest. Some RFID readers may potentially produce electromagnetic fields of sufficient amplitude and/or frequency to interact with an implanted cardiac device. Whether or not an RFID reader will interfere with an implanted pacemaker or defibrillator depends on a . While many electronic devices are safe to use if you have a pacemaker or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), there are some you should be leery of — primarily those that use magnetic chargers.
A study published this month in a medical journal shows that while interrogators of passive RFID tags do cause some electromagnetic interference to implantable pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), the devices pose no urgent health risks.A January 2010 study published in a medical journal showed that while interrogators of passive RFID tags do cause some electromagnetic interference to implantable pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), the devices pose no urgent health risks.

Although implanted cardiac pacemakers and defibrillators are designed to function normally around most appliances and equipment, patients and their cardiologists should be aware that RFID readers may be a potential source of EMI and could have temporary effects on implanted cardiac devices.
Jan. 9 -- FRIDAY, Jan. 8 (HealthDay News) -- A new study from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and pacemaker manufacturers confirms that emissions from readers of ubiquitous radio frequency identification devices (RFIDs) can interfere with pacemakers, although that risk is . While being exposed to each of the two 134 kHz RFID readers, a pacemaker reaction was observed for 34 of the 44 possible tests (77%). The same story is true for implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), devices used to . A total of 18 pacemakers and 19 Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators (ICDs) from five of the leading pacemaker and ICD manufacturers were tested for immunity to Radio Frequency (RF) emissions.
what is rfid technology
The RFID technologies that were most compatible with implantable pacemakers and ICDs in our testing were UHF RFID and continuous-wave RFID readers. Maintaining a reasonable separation distance between RFID readers and implantable pacemakers and ICDs will also help mitigate EMI.
iphone 12 and pacemaker interference

The ACR122U NFC Reader is a PC-linked contactless smart card reader/writer developed .
pace makers and rfid readers|what is rfid technology