rfid reader nfc tag Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed . NFC Device on an iPhone: It may just not be compatible with an iPhone. So ask the device's manufacturer if it is compatible with your device. Provide them with the model and the iOS version (Go to: Settings > General > About). NFC works automatically in the background on the iPhone XR when the phone is awake.Edit: maybe leverage the ability to write and read URLs to NFC tags. You need something to .
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid tags pros and cons
2 · pros and cons of nfc
3 · nfc tags are always passive
4 · nfc disadvantages
5 · different types of rfid tags
6 · differences between rfid and nfc
7 · are nfc tags waterproof
If you encounter the “Couldn’t read NFC tag” error, it’s imperative to ensure that your device’s software is up to date, as software updates often include bug fixes, performance .
RFID is a one-trick tech: A reader detects and pulls information from a tag. That's about the extent of these systems. NFC is more complex. As you just read, NFC duplicates . Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental .RFID is a one-trick tech: A reader detects and pulls information from a tag. That's about the extent of these systems. NFC is more complex. As you just read, NFC duplicates RFID's feat by reading smart tags, thanks to its read/write operation mode. Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed .
An NFC device is able to act both as a reader and as a tag. This unique ability has made NFC a popular choice for contactless payment, a key driver in the decision by influential players in the mobile industry to include NFC in newer smartphones.
Not only can a smartphone read and write data on an NFC tag or card, but it can also access detailed metadata, launch apps or URLs when the tag is scanned, and even share data between handsets via NFC's peer-to-peer (P2P) communication. NFC is a newer, high-frequency version of RFID, and also involves both tags and readers. NFC's higher frequency means that, while it can transfer data much faster than RFID, it only works from a distance of about 4 cm/1.6 in or less. Meanwhile, RFID works from a distance of up to 12 m/40 ft. NFC tags and readers communicate wirelessly with each other over very short distances. Tags store a small amount of data on them that is sent to the reader in the form of electromagnetic.
RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. This feature makes NFC more suitable for interactive applications.
The system based on NFC technology is usually comprised of an initiator (a reader) and a target (tag, card, sticker or a key fob). NFC tags contain data and tend to be read-only. These tags can securely hold personal data, with . While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.NFC devices are specifically designed to read NFC tags that operate at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high frequency (HF) RFID band. However it’s important to note that RFID technology operates across frequency ranges, including low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra high frequency (UHF).RFID is a one-trick tech: A reader detects and pulls information from a tag. That's about the extent of these systems. NFC is more complex. As you just read, NFC duplicates RFID's feat by reading smart tags, thanks to its read/write operation mode.
Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed . An NFC device is able to act both as a reader and as a tag. This unique ability has made NFC a popular choice for contactless payment, a key driver in the decision by influential players in the mobile industry to include NFC in newer smartphones. Not only can a smartphone read and write data on an NFC tag or card, but it can also access detailed metadata, launch apps or URLs when the tag is scanned, and even share data between handsets via NFC's peer-to-peer (P2P) communication. NFC is a newer, high-frequency version of RFID, and also involves both tags and readers. NFC's higher frequency means that, while it can transfer data much faster than RFID, it only works from a distance of about 4 cm/1.6 in or less. Meanwhile, RFID works from a distance of up to 12 m/40 ft.
NFC tags and readers communicate wirelessly with each other over very short distances. Tags store a small amount of data on them that is sent to the reader in the form of electromagnetic.
rfid vs nfc difference
rfid tags pros and cons
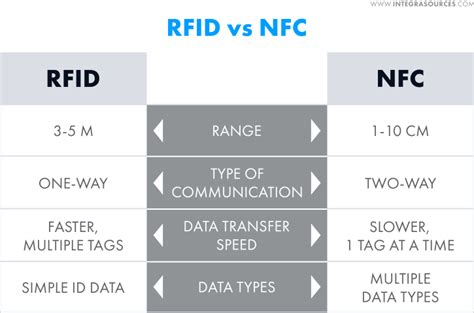

RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. This feature makes NFC more suitable for interactive applications.
The system based on NFC technology is usually comprised of an initiator (a reader) and a target (tag, card, sticker or a key fob). NFC tags contain data and tend to be read-only. These tags can securely hold personal data, with .
While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.

pros and cons of nfc
nfc tags are always passive
RFID tag NFC Key fob. Smart rfid tag epoxy nfc tag. Wholesale waterproof plastic ABS NFC .
rfid reader nfc tag|are nfc tags waterproof