nfc tag rfid reader Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed .
20 pcs NFC Cards Printable Inkjet NFC tags Programmable Ntag215 Inkjet PVC Cards NFC .
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid tags pros and cons
2 · pros and cons of nfc
3 · nfc tags are always passive
4 · nfc disadvantages
5 · different types of rfid tags
6 · differences between rfid and nfc
7 · are nfc tags waterproof
Because a ‘naked’ Rolex commands less than a full set with boxes and papers, some unscrupulous sellers have decided to buy fake warranty cards to add them to those ‘naked’ watches and leave no money on the table.
NFC tags and readers communicate wirelessly with each other over very short distances. Tags store a small amount of data on them that is sent to . NFC is a newer, high-frequency version of RFID, and also involves both tags and readers. NFC's higher frequency means that, while it can transfer data much faster than RFID, . NFC tags and readers communicate wirelessly with each other over very short distances. Tags store a small amount of data on them that is sent to the reader in the form of electromagnetic pulses.RFID is a one-trick tech: A reader detects and pulls information from a tag. That's about the extent of these systems. NFC is more complex. As you just read, NFC duplicates RFID's feat by reading smart tags, thanks to its read/write operation mode.
NFC is a newer, high-frequency version of RFID, and also involves both tags and readers. NFC's higher frequency means that, while it can transfer data much faster than RFID, it only works from a distance of about 4 cm/1.6 in or less. Meanwhile, RFID works from a distance of up to 12 m/40 ft. Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed . RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification and is a wireless, non-contact based technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags. These tags are often either attached to an object (e.g. vehicles, equipment, etc.) or implemented in an access card often used in personnel access control solutions. NFC is designed to be a secure form of data exchange, and an NFC device is capable of being both an NFC reader and an NFC tag. This unique feature allows NFC devices to communicate peer-to-peer. Long Answer: By definition, RFID is the method of uniquely identifying items using radio waves.
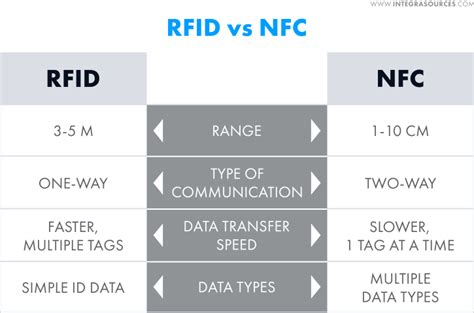
Once the initial handshake is complete, stored data on the tag is wirelessly transmitted to the reader. NFC is based on RFID technology but has a much lower transmission range. The key.The ST25 product family offers a complete portfolio of NFC tag ICs and dynamic tag ICs, as well as NFC reader ICs for a wide variety of wireless applications. ST25 products are certified by the NFC Forum, ensuring interoperability.RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. This feature makes NFC more suitable for interactive applications. With NFC tag readers, businesses can quickly and accurately track and locate assets or inventory items by scanning the NFC tags. This enables real-time visibility, reduces human errors, and improves efficiency in supply chain operations.
NFC tags and readers communicate wirelessly with each other over very short distances. Tags store a small amount of data on them that is sent to the reader in the form of electromagnetic pulses.RFID is a one-trick tech: A reader detects and pulls information from a tag. That's about the extent of these systems. NFC is more complex. As you just read, NFC duplicates RFID's feat by reading smart tags, thanks to its read/write operation mode.
NFC is a newer, high-frequency version of RFID, and also involves both tags and readers. NFC's higher frequency means that, while it can transfer data much faster than RFID, it only works from a distance of about 4 cm/1.6 in or less. Meanwhile, RFID works from a distance of up to 12 m/40 ft. Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed . RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification and is a wireless, non-contact based technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags. These tags are often either attached to an object (e.g. vehicles, equipment, etc.) or implemented in an access card often used in personnel access control solutions. NFC is designed to be a secure form of data exchange, and an NFC device is capable of being both an NFC reader and an NFC tag. This unique feature allows NFC devices to communicate peer-to-peer. Long Answer: By definition, RFID is the method of uniquely identifying items using radio waves.
Once the initial handshake is complete, stored data on the tag is wirelessly transmitted to the reader. NFC is based on RFID technology but has a much lower transmission range. The key.The ST25 product family offers a complete portfolio of NFC tag ICs and dynamic tag ICs, as well as NFC reader ICs for a wide variety of wireless applications. ST25 products are certified by the NFC Forum, ensuring interoperability.RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. This feature makes NFC more suitable for interactive applications.
adcb smart saver credit card
rfid vs nfc difference
rfid tags pros and cons
pros and cons of nfc

$15.99
nfc tag rfid reader|rfid tags pros and cons