epc rfid tag memory RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags consist of various memory types, including user memory, TID (Tag Identification), and EPC (Electronic Product Code) memory. . Use V1CE NFC business cards to connect easily. Tap to share your details, follow up smoothly, and make a lasting impression. A simple, eco-friendly way to network better. . Metal NFC .
0 · what is epc in rfid
1 · what is epc data
2 · epcglobal gen2
3 · epc rfid gen 3
4 · epc gen 2 rfid
5 · epc codes lookup
6 · epc barcode
7 · decode identifier
Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags consist of various memory types, including user memory, TID (Tag Identification), and EPC (Electronic Product Code) memory. .Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags consist of various memory types, including user memory, TID (Tag Identification), and EPC (Electronic Product Code) memory. EPC memory is a crucial component of RFID technology, assigned as a .
The Electronic Product Code (EPC) is a globally unique identifier that enables the tracking and management of products throughout the supply chain using RFID technology. The EPC is stored in the RFID tag’s memory and can be read by RFID readers.
What are the different types of memory in RFID tags? RFID tags can store significantly more data than UPC-12 or EAN-13 barcodes. GS1 defines the EPC (Electronic Product Code) tag data standards including the data that is encoded in EPC-encoded RAIN RFID tags namely the EPC, User Memory data, control information, and tag manufacture information.
An ultrahigh-frequency Gen 2 RFID tag carries business data in two memory banks: the EPC memory bank (also called the UII memory bank) and the user memory bank.
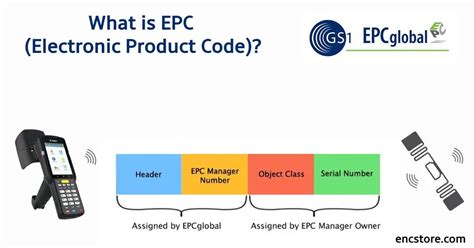
Discover the significance of EPC memory and User memory in UHF RFID labels. This comprehensive guide sheds light on their unique functions and differences, helping you optimize your RFID system.The EPC is a unique identifier that an information system can use to refer to a specific physical object. An RFID tag is a data carrier that can be used to physically affix an EPC identifier to the object it identifies. The EPC is identifier data that is stored inside the memory of the RFID tag.
This interactive application decodes the contents of the user memory bank of an EPC/RFID tag and displays the data elements it contains, following the EPC Tag Data Standard (TDS) 1.13. Find more here.2. EPC memory. This memory bank is designed to contain the EPC code, or Electronic Product Code, the GS1 standard that uniquely identifies retail products. That said, the EPC memory can be used freely, for programming personal codes, service numbers, inventory numbers, serial numbers and so on. EPC memory has a minimum of 96 bits of writable .
Gen 2 UHF RFID tags are comprised of an antenna and a chip (more accurately called an integrated circuit, or IC). In this article, we will walk through the 4 memory banks on the IC inside of a UHF RFID tag and when to use each. Gen 2 tags contain four types of memory: Reserved memory. EPC memory. TID memory.
Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags consist of various memory types, including user memory, TID (Tag Identification), and EPC (Electronic Product Code) memory. EPC memory is a crucial component of RFID technology, assigned as a .The Electronic Product Code (EPC) is a globally unique identifier that enables the tracking and management of products throughout the supply chain using RFID technology. The EPC is stored in the RFID tag’s memory and can be read by RFID readers.
What are the different types of memory in RFID tags? RFID tags can store significantly more data than UPC-12 or EAN-13 barcodes. GS1 defines the EPC (Electronic Product Code) tag data standards including the data that is encoded in EPC-encoded RAIN RFID tags namely the EPC, User Memory data, control information, and tag manufacture information. An ultrahigh-frequency Gen 2 RFID tag carries business data in two memory banks: the EPC memory bank (also called the UII memory bank) and the user memory bank.Discover the significance of EPC memory and User memory in UHF RFID labels. This comprehensive guide sheds light on their unique functions and differences, helping you optimize your RFID system.
The EPC is a unique identifier that an information system can use to refer to a specific physical object. An RFID tag is a data carrier that can be used to physically affix an EPC identifier to the object it identifies. The EPC is identifier data that is stored inside the memory of the RFID tag.This interactive application decodes the contents of the user memory bank of an EPC/RFID tag and displays the data elements it contains, following the EPC Tag Data Standard (TDS) 1.13. Find more here.2. EPC memory. This memory bank is designed to contain the EPC code, or Electronic Product Code, the GS1 standard that uniquely identifies retail products. That said, the EPC memory can be used freely, for programming personal codes, service numbers, inventory numbers, serial numbers and so on. EPC memory has a minimum of 96 bits of writable .
bluetooth smart card reader for iphone
Depending on the iPhone model, there are different ways to use the NFC function. Starting with iOS 14, the “NFC Tag Reader” function is available by default to all users who have at least an iPhone 7. So if you own an iPhone 7 or newer, you no longer . See more
epc rfid tag memory|decode identifier