are rfid tags active or passive The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases.
NFC RFID Example with Arduino. Her we will define the PN532 as a reader for NTAGS. Every NTAGS card has a code that is viewable and changeable with PN532. To do that programming will be required for different functions. First, .Download the Adafruit PN532 library from github. Uncompress the folder and rename the folder Adafruit_PN532. Inside the folder you should see the Adafruit_PN532.cpp and Adafruit_PN532.h files. Install the Adafruit_PN532 .
0 · where are active rfid used
1 · rfid active and passive tags
2 · long range active rfid tags
3 · how expensive are rfid tags
4 · examples of active rfid tags
5 · active rfid tags price
6 · active rfid tags cost
7 · active rfid tags and readers
$24.98
There are two kinds of RFID systems that exist- passive and active. If you're new to RFID, you might be wondering what the difference is between these types, and which one is best for your application. Below, we provide a short answer to these questions and more along with a more complex, long-form answer. See morePassive RFID systems use tags with no internal power source and instead are powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an . See more Unlike active RFID tags, passive RFID tags only have two main components – the tag's antenna, and the microchip or integrated circuit (IC). As the name implies, passive tags wait for a signal from an RFID reader. The main difference between active and passive RFID tags is that an active tag has a battery while a passive tag does not. Many commercially used tags are passive, owing to their significantly lower cost, long life and small size.
What are the key differences between active RFID and passive RFID. Four key differences exist between active and passive RFID tags: signal range, cost and lifespan, tag size and suitable attachment methods, and real-time monitoring vs. scanner-based activation.
The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases. Within the realm of RFID technology, two primary tag categories exist: active and passive RFID tags. Each category exhibits distinct characteristics and functionalities that cater to diverse operational requirements.
There are two categories of tags: active RFID tags with their own power source, and passive RFID tags powered by the reader’s electromagnetic field. How does passive RFID work? Passive RFID tags play a crucial role in asset and inventory management.Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader.
where are active rfid used
When implementing an active RFID system to track assets, businesses require a reader, an active tag, and an antenna. Unlike a passive tag, which has no internal power source, an active RFID tag will feature a long-lasting battery. This allows it to continuously send signals and transmit data stored on a tag. Active RFID tags have their own power source and are ideal for real-time asset tracking, while passive RFID tags rely on energy from RFID readers and are cost-effective for applications like access control and supply chain management.Depending on the power supply method, RFID tags can be divided into two categories: active RFID tags and passive RFID tags. Understanding the working principles, characteristics and application scenarios of these two tags is crucial for enterprises to choose the type of tags that best suits their needs. What are active RFID tags?
Unlike active RFID tags, passive RFID tags only have two main components – the tag's antenna, and the microchip or integrated circuit (IC). As the name implies, passive tags wait for a signal from an RFID reader.
The main difference between active and passive RFID tags is that an active tag has a battery while a passive tag does not. Many commercially used tags are passive, owing to their significantly lower cost, long life and small size.
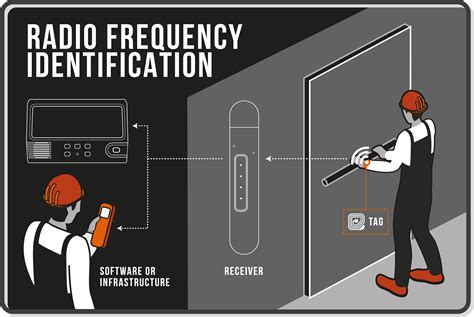
What are the key differences between active RFID and passive RFID. Four key differences exist between active and passive RFID tags: signal range, cost and lifespan, tag size and suitable attachment methods, and real-time monitoring vs. scanner-based activation. The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases. Within the realm of RFID technology, two primary tag categories exist: active and passive RFID tags. Each category exhibits distinct characteristics and functionalities that cater to diverse operational requirements. There are two categories of tags: active RFID tags with their own power source, and passive RFID tags powered by the reader’s electromagnetic field. How does passive RFID work? Passive RFID tags play a crucial role in asset and inventory management.
Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader.When implementing an active RFID system to track assets, businesses require a reader, an active tag, and an antenna. Unlike a passive tag, which has no internal power source, an active RFID tag will feature a long-lasting battery. This allows it to continuously send signals and transmit data stored on a tag. Active RFID tags have their own power source and are ideal for real-time asset tracking, while passive RFID tags rely on energy from RFID readers and are cost-effective for applications like access control and supply chain management.
your slim rfid credit card protector wallet

wireless rfid reader for sale
The ACR1255U-J1 ACS Secure Bluetooth® NFC Reader supports ISO 14443 Type A and B smart cards, MIFARE®, FeliCa, and most NFC tags and devices compliant with ISO 18092 standard. The ACR1255U-J1 has both .
are rfid tags active or passive|active rfid tags price