how does nfc rfid tag gets power When an RFID tag comes into the range of an RFID reader, it receives radio waves from the reader, which provide the necessary energy to power the tag. The tag then uses this energy to power its microchip, allowing it . TIGER TALK. Thursdays at 6 p.m. CT. Hosted by Brad Law and the Voice of .
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid tags pros and cons
2 · pros and cons of nfc
3 · nfc tags are always passive
4 · nfc disadvantages
5 · different types of rfid tags
6 · differences between rfid and nfc
7 · are nfc tags waterproof
The Drive with Bill Cameron, ESPN 106.7’s weekday afternoon sports show, is a fast-paced, in-depth look at the world of sports with a focus on Auburn University and local high schools. Live from 4:00 p.m.-6:00 p.m., the show has been .
The ST25DV has an energy harvesting output pin, on which different resistor values where applied. Meanwhile the field was observed with a simple loop antenna and an oscilloscope. The smartphone was attached directly on the ST25 board, making sure the 2 . NFC tags are passive, meaning they don't have any power source. Instead, they literally draw power from the device that reads them, thanks to magnetic induction . When a .
The coil allows the tag to wirelessly receive power from the NFC reader through a process known as electromagnetic induction. Essentially, . What is the maximum power an NFC-enabled card can draw from a contactless payment terminal? What are the determinants (i.e. card reader voltage)? What techniques are . When an RFID tag comes into the range of an RFID reader, it receives radio waves from the reader, which provide the necessary energy to power the tag. The tag then uses this energy to power its microchip, allowing it . The tags contain chips that are energised through the RF field that provides enough power for them to start up, at which point they can communicate with a host computer .
Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags are one application of inductive coupling. This technology is a predecessor to NFC. With an RFID tag, an electronic reader generates a magnetic field. Bringing an RFID tag close to . The ST25DV has an energy harvesting output pin, on which different resistor values where applied. Meanwhile the field was observed with a simple loop antenna and an oscilloscope. The smartphone was attached directly on the ST25 board, making sure the 2 coils are coupled in an optimal way.NFC tags are passive, meaning they don't have any power source. Instead, they literally draw power from the device that reads them, thanks to magnetic induction . When a reader gets close enough to a tag, it energizes it and transfer data from that tag.
The coil allows the tag to wirelessly receive power from the NFC reader through a process known as electromagnetic induction. Essentially, whenever you bring a powered NFC reader near the. What is the maximum power an NFC-enabled card can draw from a contactless payment terminal? What are the determinants (i.e. card reader voltage)? What techniques are available for harvesting this c. When an RFID tag comes into the range of an RFID reader, it receives radio waves from the reader, which provide the necessary energy to power the tag. The tag then uses this energy to power its microchip, allowing it to transmit its stored information back to the reader.
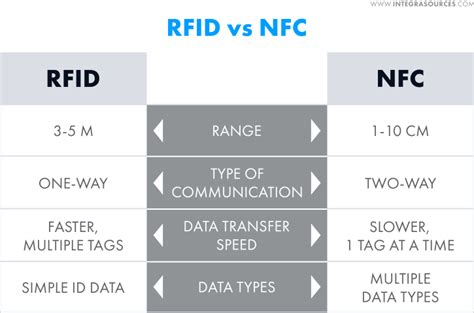
rfid vs nfc difference
The tags contain chips that are energised through the RF field that provides enough power for them to start up, at which point they can communicate with a host computer for whatever their. Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags are one application of inductive coupling. This technology is a predecessor to NFC. With an RFID tag, an electronic reader generates a magnetic field. Bringing an RFID tag close .
Most RFID tags are unpowered, so when the antenna in the tag picks up radio waves from the reader, it generates a small amount of electricity. That electricity activates the chip inside the tag, and it sends a signal with the information stored on the chip back to the reader.
When an NFC reader is close to an NFC tag, the electromagnetic waves emitted by the reader generate an induced current in the tag’s antenna, which powers up the tag’s chip. The NFC tag then activates the internal chip after it has received enough energy.
Near Field Communication is a technology standard based on Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) that does not require an internal power source to function and can transmit information wirelessly over small distances. As a result NFC opens up new possibilities for consumer goods.
The ST25DV has an energy harvesting output pin, on which different resistor values where applied. Meanwhile the field was observed with a simple loop antenna and an oscilloscope. The smartphone was attached directly on the ST25 board, making sure the 2 coils are coupled in an optimal way.NFC tags are passive, meaning they don't have any power source. Instead, they literally draw power from the device that reads them, thanks to magnetic induction . When a reader gets close enough to a tag, it energizes it and transfer data from that tag. The coil allows the tag to wirelessly receive power from the NFC reader through a process known as electromagnetic induction. Essentially, whenever you bring a powered NFC reader near the.
What is the maximum power an NFC-enabled card can draw from a contactless payment terminal? What are the determinants (i.e. card reader voltage)? What techniques are available for harvesting this c. When an RFID tag comes into the range of an RFID reader, it receives radio waves from the reader, which provide the necessary energy to power the tag. The tag then uses this energy to power its microchip, allowing it to transmit its stored information back to the reader. The tags contain chips that are energised through the RF field that provides enough power for them to start up, at which point they can communicate with a host computer for whatever their.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags are one application of inductive coupling. This technology is a predecessor to NFC. With an RFID tag, an electronic reader generates a magnetic field. Bringing an RFID tag close . Most RFID tags are unpowered, so when the antenna in the tag picks up radio waves from the reader, it generates a small amount of electricity. That electricity activates the chip inside the tag, and it sends a signal with the information stored on the chip back to the reader.When an NFC reader is close to an NFC tag, the electromagnetic waves emitted by the reader generate an induced current in the tag’s antenna, which powers up the tag’s chip. The NFC tag then activates the internal chip after it has received enough energy.
rfid tags pros and cons
trac fone smart phone cards
transfer money from money travel card to smart access
translink top up smart card
pros and cons of nfc
WFAN Sports Radio: KIRO Radio 97.3 FM: Republic Broadcasting Network: WTMA: 96.3 Newsradio KKOB: WLQY 1320 AM: Radio International 1600 AM: 1510 WMEX: Z102.9: AM 1370 KDTH: WIKY-FM: Radio Hamrah: .
how does nfc rfid tag gets power|different types of rfid tags