active rfid tags interference The HF band operates between 3 and 30 MHz, with most HF RFID systems at 13.56 MHz. These systems typically offer read ranges from 10 cm to 1 m and exhibit moderate sensitivity to interference. HF RFID is widely used in . $39.00
0 · what is rfid technology
1 · rfid problems with tags
2 · rfid problems
3 · radio frequency rfid tags
4 · radio frequency identification technology
5 · interference with rfid
6 · active rfid tags
News: News and events about NFC (Near Field Communication), contactless .
what is rfid technology
Active tags that use IEE802.11 WIFI standards could experience difficulty when used alongside WIFI networks operating to the same standards. Whilst in laboratory conditions it has been shown that electro-magnetic radiation from RFID can cause interference with other systems.NFC operates in the high-frequency RFID spectrum at 13.56MHz so it can only .
rfid problems with tags
RFID tags can be used to tell applications what things are, where things are, if .
Different standards apply to the different frequencies used for tags – whether .
The HF band operates between 3 and 30 MHz, with most HF RFID systems at 13.56 MHz. These systems typically offer read ranges from 10 cm to 1 m and exhibit moderate sensitivity to interference. HF RFID is widely used in .
Active tags that use IEE802.11 WIFI standards could experience difficulty when used alongside WIFI networks operating to the same standards. Whilst in laboratory conditions it has been shown that electro-magnetic radiation from RFID can cause interference with other systems.
The HF band operates between 3 and 30 MHz, with most HF RFID systems at 13.56 MHz. These systems typically offer read ranges from 10 cm to 1 m and exhibit moderate sensitivity to interference. HF RFID is widely used in ticketing, payment, and data transfer applications.One hazardous incident at 25 cm occurred during 41 device tests with the active RFID tag of the 125-kHz RFID system. It caused interference in the atrial and ventricular electrogram curve read by the pacemaker programmer which could potentially induce inappropriate inhibition.
Adjusting the frequency, adding shielding, or optimizing antenna design can effectively reduce interference. How to Optimize RFID Tag Range. Here are three ways to improve the read range of RFID tags: Choose the Right RFID Tag: When selecting a tag, consider the specific needs of your application. Passive tags are ideal for short-range .
rfid problems
Active systems involve either tags waking up and broadcasting their signal every few seconds or minutes, or a reader emitting a signal that activates the tag. The tags generally do not cause much interference, because they emit very little energy for very brief intervals. Interference from other radio-frequency (RF) emitting devices (RFI), such as other RFID readers and Wi-Fi access points, can negatively impact RFID system performance. Active RFID systems tend to be more expensive than passive ones, though Bluetooth-based tags cost as little as one US dollar at the low end. However, Bluetooth Low Energy is more susceptible to performance and interference issues. Premium variants can cost more than a hundred dollars.High Anti-interference Capability. The active signal transmission mechanism enables it to work stably even in interference environments. It can work stably whether in an environment with high electromagnetic interference or in the presence of a large .
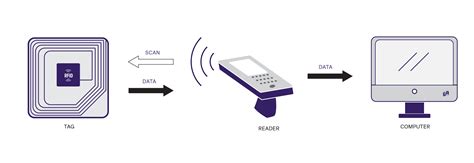
Active tags contain a power source (e.g., battery) and permit higher read ranges and/or lower reader power. Passive tags, on the other hand, draw power from the incident electromagnetic waves of the reader and, hence, are lower in cost. Active RFID tags, distinguished by their internal power source, operate using a battery to actively transmit signals to RFID readers. The inclusion of a power source empowers active tags to broadcast signals over longer distances, enabling read ranges that can extend up to hundreds of meters.Active tags that use IEE802.11 WIFI standards could experience difficulty when used alongside WIFI networks operating to the same standards. Whilst in laboratory conditions it has been shown that electro-magnetic radiation from RFID can cause interference with other systems.
The HF band operates between 3 and 30 MHz, with most HF RFID systems at 13.56 MHz. These systems typically offer read ranges from 10 cm to 1 m and exhibit moderate sensitivity to interference. HF RFID is widely used in ticketing, payment, and data transfer applications.
One hazardous incident at 25 cm occurred during 41 device tests with the active RFID tag of the 125-kHz RFID system. It caused interference in the atrial and ventricular electrogram curve read by the pacemaker programmer which could potentially induce inappropriate inhibition.
Adjusting the frequency, adding shielding, or optimizing antenna design can effectively reduce interference. How to Optimize RFID Tag Range. Here are three ways to improve the read range of RFID tags: Choose the Right RFID Tag: When selecting a tag, consider the specific needs of your application. Passive tags are ideal for short-range .Active systems involve either tags waking up and broadcasting their signal every few seconds or minutes, or a reader emitting a signal that activates the tag. The tags generally do not cause much interference, because they emit very little energy for very brief intervals. Interference from other radio-frequency (RF) emitting devices (RFI), such as other RFID readers and Wi-Fi access points, can negatively impact RFID system performance. Active RFID systems tend to be more expensive than passive ones, though Bluetooth-based tags cost as little as one US dollar at the low end. However, Bluetooth Low Energy is more susceptible to performance and interference issues. Premium variants can cost more than a hundred dollars.
High Anti-interference Capability. The active signal transmission mechanism enables it to work stably even in interference environments. It can work stably whether in an environment with high electromagnetic interference or in the presence of a large . Active tags contain a power source (e.g., battery) and permit higher read ranges and/or lower reader power. Passive tags, on the other hand, draw power from the incident electromagnetic waves of the reader and, hence, are lower in cost.
smart card reader tcp ip
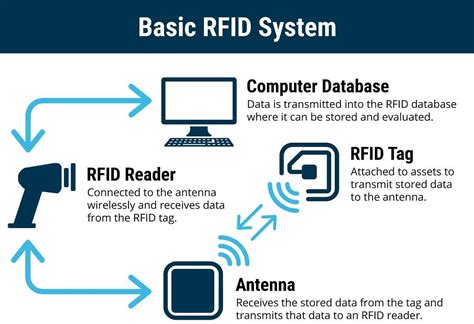
radio frequency rfid tags
radio frequency identification technology
interference with rfid
RFID is a one-trick tech: A reader detects and pulls information from a tag. That's about the .NFC enabled phones can ONLY read NFC and passive high frequency RFID (HF-RFID). These must be read at an extremely close range, .
active rfid tags interference|radio frequency identification technology