uhf rfid is better than rfid only RFID HF operates in the High-Frequency range of 13.56 MHz, while RFID UHF operates in the Ultra-High Frequency range of 860-960 MHz. The variation in frequency is a fundamental distinction that leads to various differences in their .
Collection of NFC Tag Keychains available in 3 shapes: nfc-tag-teardrop: a 38 .Anti-Tamper NFC Tag; Epoxy Rod Tag; Fibre66 Rod Tag; iButton Key Tag; Jewelry Retail Tag; .
0 · rfid vs low frequency
1 · rfid frequency
2 · low frequency rfid range
3 · high frequency rfid tags
4 · high frequency rfid 12 inch
5 · hf rf frequency
Wholesale custom size NFC inlay 13.56MHz wet inlay NFC tag/label/sticker at the best price on RFIDSilicone.com. Contact: [email protected] . Custom material, size, antenna, etc. .RAIN RFID inlays, tags and labels work in the Ultra-High Frequency Band and can provide a read range of up to 10 meters or 30 feet. This makes RAIN RFID systems ideal for many tracking applications. Near field communication (NFC) .
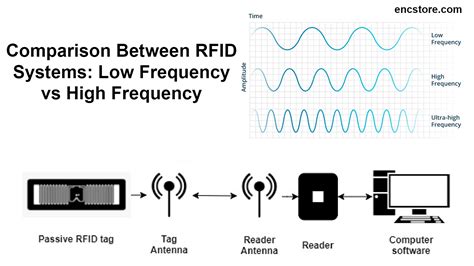
One of the most obvious differences between Low Frequency RFID and High Frequency RFID is the frequency range on which the tags and readers communicate. Low Frequency RFID typically operates between 125 kHz and 134 kHz, but the overall, larger range is between 30 kHz and 300 kHz. The . See moreData rates, also known as data-transfer rates, describe how fast the data from the tag can be transferred to the RFID reader. When comparing the data rates of Low Frequency RFID and . See more
Most High Frequency RFID tags, including NFC tags, have data that can be read and re-written hundreds of times, but the same cannot be . See moreBoth Low Frequency RFID and High Frequency RFID are short range RFID frequencies, and neither one can reliably read tags over 1 foot in read distance. In some RFID . See moreIf you are familiar with Passive UHF RFID tags, you are aware that these tags must be used with precautions around metal, liquids, and other difficult environmental factors. UHF RFID . See moreRFID HF operates in the High-Frequency range of 13.56 MHz, while RFID UHF operates in the Ultra-High Frequency range of 860-960 MHz. The variation in frequency is a fundamental distinction that leads to various differences in their .
rfid vs low frequency
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.
does the iphone have a nfc reader
RFID HF operates in the High-Frequency range of 13.56 MHz, while RFID UHF operates in the Ultra-High Frequency range of 860-960 MHz. The variation in frequency is a fundamental distinction that leads to various differences in their applications and performances. Ambient IoT is relatively new compared to UHF RFID, the latest version of which was standardized at the turn of the millennium. While the technology further amplifies the benefits created by RFID through improved supply chain visibility, .
RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.The two RFID frequency bands, HF vs UHF, have obvious differences in terms of application areas, technical characteristics and advantages. When enterprises choose to use which RFID frequency band, should fully consider their own needs and the performance and cost trade-offs. UHF RFID tags are considered the “supply chain frequency” because they’re generally lower priced than the other types, while still providing good read ranges and rates. Common applications include item-level tracking, retail inventory control and .
Reduce shrinkage and prevent inventory stock-outs. Secure access to specified areas or products. Improve overall business operations. Understanding the differences between HF and UHF RFID technology can change the way you do business and . In UHF systems, the electric field powers up the tag passing within the energy field. The power of the electric field is used for the RFID tag’s circuitry in a similar way to HF tags, but through capacitive coupling instead of inductive coupling.When considering RFID technology, one important decision that needs to be made is whether to use HF (High Frequency) or UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the differences between these two technologies and provide insights to help you choose the right one for your specific needs. Typically, passive RFID systems use either low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), or ultra-high frequency (UHF). Based on a schematic overview, this blog article provides an initial guide to these frequency ranges and their characteristics.
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.RFID HF operates in the High-Frequency range of 13.56 MHz, while RFID UHF operates in the Ultra-High Frequency range of 860-960 MHz. The variation in frequency is a fundamental distinction that leads to various differences in their applications and performances. Ambient IoT is relatively new compared to UHF RFID, the latest version of which was standardized at the turn of the millennium. While the technology further amplifies the benefits created by RFID through improved supply chain visibility, .
RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.The two RFID frequency bands, HF vs UHF, have obvious differences in terms of application areas, technical characteristics and advantages. When enterprises choose to use which RFID frequency band, should fully consider their own needs and the performance and cost trade-offs.
UHF RFID tags are considered the “supply chain frequency” because they’re generally lower priced than the other types, while still providing good read ranges and rates. Common applications include item-level tracking, retail inventory control and .Reduce shrinkage and prevent inventory stock-outs. Secure access to specified areas or products. Improve overall business operations. Understanding the differences between HF and UHF RFID technology can change the way you do business and . In UHF systems, the electric field powers up the tag passing within the energy field. The power of the electric field is used for the RFID tag’s circuitry in a similar way to HF tags, but through capacitive coupling instead of inductive coupling.When considering RFID technology, one important decision that needs to be made is whether to use HF (High Frequency) or UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the differences between these two technologies and provide insights to help you choose the right one for your specific needs.
Auburn Sports Network game day coverage begins three hours prior to kickoff. Tiger Talk, Auburn's popular weekly radio show, returns on Thursday nights at 6 p.m. CT .
uhf rfid is better than rfid only|rfid frequency