uhf rfid interference Here are some key ways interference can affect the functionality and efficiency of UHF RFID systems: Data Corruption and Loss: Issue: Interference can lead to corrupted . Method 2: Looking for signs on the card: Some cards may have visible indications indicating the presence of RFID or NFC technology. Look for any logos or symbols on the card that suggest contactless communication. .Tapping to pay with your Visa contactless card or payment-enabled mobile/wearable device is .
0 · what is rfid technology
1 · rfid problems with tags
2 · rfid problems and solutions
3 · rfid problems
4 · interference with rfid
Created in 1989, amended in 1992 (addition of the T=1 protocol), amended in 1994 (revision of Protocol Type Selection), updated in 1997 (including addition of 3 Volt operation), amended in 2002 (including addition of 1.8 Volt operation), last updated in . See more
Here are some key ways interference can affect the functionality and efficiency of UHF RFID systems: Data Corruption and Loss: Issue: Interference can lead to corrupted .UHF systems can suffer interference due to reflection or re-radiation of power signals. These make careful site planning and antenna or reader tuning essential. Passive or semi-passive systems create less risk of interference than active ones.
UHF systems can suffer interference due to reflection or re-radiation of power signals. These make careful site planning and antenna or reader tuning essential. Passive or semi-passive systems create less risk of interference than active ones. Here are some key ways interference can affect the functionality and efficiency of UHF RFID systems: Data Corruption and Loss: Issue: Interference can lead to corrupted communication between RFID readers and tags.
This paper investigates the effects of RF interference be-tween a passive UHF RFID system and a communications sys-tem sharing the 902 MHz to 928 MHz industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) band. So, let’s explore the various interference issues in RFID, understanding the impact of low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF) on interference, as well as the challenges posed by metals and liquids. While radio frequency identification (RFID) has a broad range of applications, this project focuses on those that are relevant to homeland security, such as tracking cargo and people at U.S. borders. In particular, we are developing test procedures to evaluate the impact on RFID of interference generated by other wireless systems. Problems with RFID include data reliability, security and privacy, electromagnetic interference and return on investment (ROI). The sources of interference for RFID installations include reader signal collisions, which occur when two or more RFID readers try to read the same tag at the same time.
In this paper, performance of a passive UHF RFID system is experimentally evaluated for potential deployment in industrial settings where many sources that generate ambient electromagnetic interference (EMI) exist.
In this paper, an experimental analysis on the interference between GSM and UHF RFID is presented. The experimental results highlight the negative effects of the use of GSM devices in the proximity of operating UHF RFID systems.
In general, there are three types of Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID interference: tag interference, multiple reader-to-tag interference and reader-to-reader interference (Kim et al., 2008)..Abstract: Channel modeling of Passive Ultra High Frequency Radio Frequency Identification (UHF RFID) with double-tag interference is a major challenge for applications in the Internet of Things, like indoor localization, warehouse management, etc.UHF systems can suffer interference due to reflection or re-radiation of power signals. These make careful site planning and antenna or reader tuning essential. Passive or semi-passive systems create less risk of interference than active ones. Here are some key ways interference can affect the functionality and efficiency of UHF RFID systems: Data Corruption and Loss: Issue: Interference can lead to corrupted communication between RFID readers and tags.
This paper investigates the effects of RF interference be-tween a passive UHF RFID system and a communications sys-tem sharing the 902 MHz to 928 MHz industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) band. So, let’s explore the various interference issues in RFID, understanding the impact of low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF) on interference, as well as the challenges posed by metals and liquids. While radio frequency identification (RFID) has a broad range of applications, this project focuses on those that are relevant to homeland security, such as tracking cargo and people at U.S. borders. In particular, we are developing test procedures to evaluate the impact on RFID of interference generated by other wireless systems. Problems with RFID include data reliability, security and privacy, electromagnetic interference and return on investment (ROI). The sources of interference for RFID installations include reader signal collisions, which occur when two or more RFID readers try to read the same tag at the same time.
In this paper, performance of a passive UHF RFID system is experimentally evaluated for potential deployment in industrial settings where many sources that generate ambient electromagnetic interference (EMI) exist.In this paper, an experimental analysis on the interference between GSM and UHF RFID is presented. The experimental results highlight the negative effects of the use of GSM devices in the proximity of operating UHF RFID systems. In general, there are three types of Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID interference: tag interference, multiple reader-to-tag interference and reader-to-reader interference (Kim et al., 2008)..
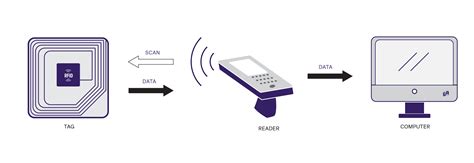
what is rfid technology
rfid problems with tags
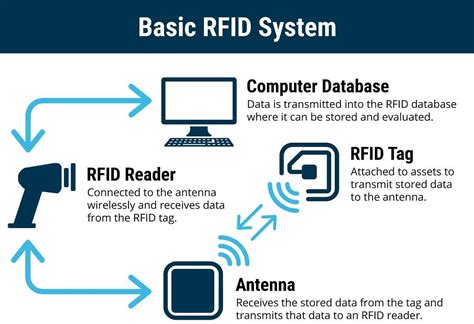
rfid problems and solutions
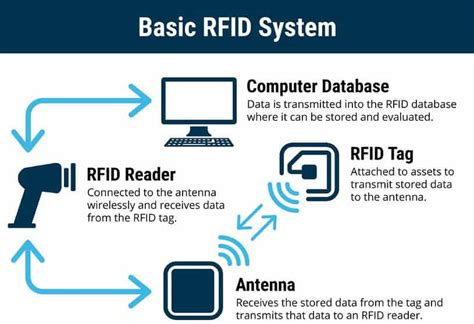
rfid problems
interference with rfid
Touch the WRITE TAG (AUTO) button and press your NTAG215 NFC tag to your .
uhf rfid interference|interference with rfid