is rfid a sensor Often the term "RFID" is loosely used to describe both, but there's a big difference between them: RF tags all send the same, simple signal and simply tell the receiver that something is present; RFID tags send more complex signals that uniquely identify whatever they're attached to.
2- Preparing to Program Your NFC Tag. 3- Step by Step Directions to Program Your NFC Tag. 3.1- Step 1: Setting Up Your NFC-Enabled Device. 3.2- Step 2: Selecting the Content for Your NFC Tag. 3.3- Step 3: Writing the .
0 · rfid sensor simulation
1 · rfid sensor price
2 · rfid sensor meaning
3 · rfid sensor full form
4 · rfid sensor datasheet
5 · rfid sensor cost
6 · rfid is involved when using
7 · rfid full form in computer
If the card is a high frequency card that your phone can read, and the student hostel only uses the serial number of the card (not the data stored on it), and you have a rooted Android phone and you have an app that can do that sort of .
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.An RFID tag can be affixed to an object and used to track tools, equipment, inventory, assets, people, or other objects. RFID offers advantages over manual systems or use of barcodes. The tag can be read if passed near a reader, even if it is covered by the object or not visible. The tag can be read inside a case, carton, box or other container, and unlike .RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.
An RFID sensor consists of two parts: an antenna and a microchip. The antenna emits radio waves that power the microchip. The microchip stores data that identifies the item it’s attached to. Often the term "RFID" is loosely used to describe both, but there's a big difference between them: RF tags all send the same, simple signal and simply tell the receiver that something is present; RFID tags send more complex signals that uniquely identify whatever they're attached to.
They have developed a new ultra-high-frequency, or UHF, RFID tag-sensor configuration that senses spikes in glucose and wirelessly transmits this information. In the future, the team plans to tailor the tag to sense chemicals and gases in .Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a low-cost wireless technology that makes possible the connection of billions of things, enabling consumers and businesses to engage, identify, locate, transact, and authenticate products [1]. Radio frequency identification (RFID) is defined as a cutting-edge technology that harnesses radio waves to identify and monitor objects or people effortlessly without physical contact. The fundamentals of the wireless sensing technology are summarized in the first part of the work, and the benefits of adopting RFID sensors for replacing standard sensor-equipped Wi-Fi nodes are discussed.
RFID (radio frequency identification) technology appeared nearly 70 years ago. Deployed more widely only from the early 2000s, it is now booming and its development is still accelerating. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and wireless RF sensors are the conduit between the physical world and the digital world because it allows physical objects to be identified and differentiated by computers.RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.
An RFID sensor consists of two parts: an antenna and a microchip. The antenna emits radio waves that power the microchip. The microchip stores data that identifies the item it’s attached to.
rfid sensor simulation
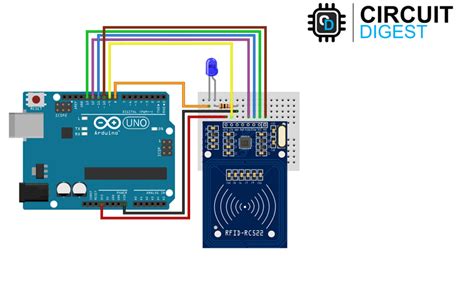
rfid sensor price
Often the term "RFID" is loosely used to describe both, but there's a big difference between them: RF tags all send the same, simple signal and simply tell the receiver that something is present; RFID tags send more complex signals that uniquely identify whatever they're attached to. They have developed a new ultra-high-frequency, or UHF, RFID tag-sensor configuration that senses spikes in glucose and wirelessly transmits this information. In the future, the team plans to tailor the tag to sense chemicals and gases in .
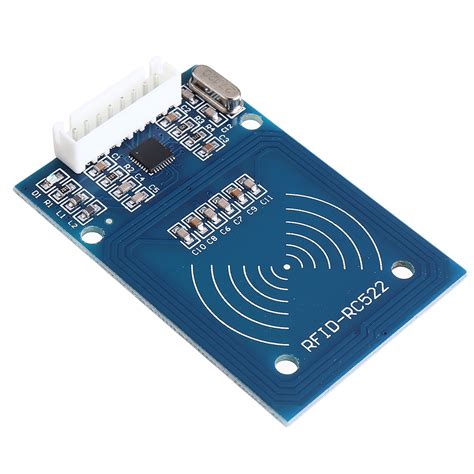

Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a low-cost wireless technology that makes possible the connection of billions of things, enabling consumers and businesses to engage, identify, locate, transact, and authenticate products [1].
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is defined as a cutting-edge technology that harnesses radio waves to identify and monitor objects or people effortlessly without physical contact. The fundamentals of the wireless sensing technology are summarized in the first part of the work, and the benefits of adopting RFID sensors for replacing standard sensor-equipped Wi-Fi nodes are discussed. RFID (radio frequency identification) technology appeared nearly 70 years ago. Deployed more widely only from the early 2000s, it is now booming and its development is still accelerating.

rfid sensor meaning

rfid uhf module
The Seattle Seahawks are not going to be participating in the 2018 NFL Playoffs. With the way they fell flat on their faces against the Arizona Cardinals, losing 26-24 in the team’s season .
is rfid a sensor|rfid is involved when using